Like previous versions of the operating system, Windows 10 supports NTFS file compression to save disk space. Unlike ZIP archiving, NTFS compression does not require the user to put the necessary files in a separate archive and then extract them for use. The system compresses files, reduces the space occupied, but the objects are ready for use at any time and do not require additional actions.
NTFS file compression works using tools built into the system and does not require the user to download or install additional software. You can compress files in Windows 10 using both Explorer and the Command Line. The latter method is more complex due to the need to remember commands and additional parameters. You will find both methods here.
The efficiency of file compression is directly proportional to the size of the object. In other words, the larger the file, the more disk space the system can save through compression. In this case, the compression time will also be directly proportional to the size of the compressed file. This simple but quite effective compression method will be useful for those who have very limited space on their computer, but at the same time need to constantly store large files locally. If you are one of those users, then it will also be useful for you to read the instructions “”. It will help you carve out a few extra gigabytes of free disk space. In addition, see the instructions for freeing up space on the system disk after installing the operating system.
Please note that compressed files and folders in Windows 10 appear with an additional icon with two arrows. This will help you figure out which files are compressed and which are not.
How to compress files in Windows 10 Explorer

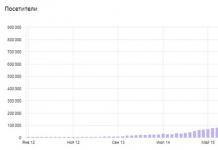
Once the changes are applied, you can evaluate the effectiveness of the compression. The screenshot shows that before compression the folder occupied 1.08 GB of disk space, and after compression the volume decreased to 0.99 GB of disk space. In this case, the savings were approximately 8%, which is quite good. 
How to decompress files in Windows 10
Everything is done in exactly the same way as file compression.

Compressing files via Command Line in Windows 10
Click Win+ R and enter cmd. In the command line window that opens, you need to enter the command compact/# “full path to file or folder”. Depending on the desired result, you will need to use the following commands:
- Compact/c “ fullThis is the path to the file or folder"– compression of one file or folder. If you compress a folder, then the compression will not affect its subfolders.
- Compact/u “ fullThis is the path to the file or folder"– recovery of one file or folder.
- Compact/c/s “ fullThis is the path to the folder"– compresses a folder with all its files or folders.
- Compact/u/s “ fullThis is the path to the file or folder"– restore the folder to its normal size with all its subfolders or files.
Additional commands for the utility compact.exe include:
- /C- Compresses user-specified files or folders. Directories will be named in such a way that all new files will also be compressed. Objects with the /EXE parameter will be excluded.
- /U- Unpacks the specified files. Directories are marked so that files added later will not be compressed. If the /EXE option is specified, only files compressed as executable files will be unpacked; if this parameter is omitted, only NTFS compressed files will be unpacked.
- /S- Performs the specified operation on files in the selected directory and all its subdirectories. The default is the current directory.
- /A- Displays files with the attributes "hidden" and "system". By default, these files are skipped.
- /I- Continues to perform the specified operation even after errors occur. By default, the COMPACT program is aborted when an error occurs.
- /F- Forces compression of all specified files, even if some of them are already compressed. By default, compressed files are skipped.
- /Q- Displays only the most essential information.
- /EXE- Uses compression optimized for executable files that are read frequently and not modified. Supported algorithms: XPRESS4K (fastest, default), XPRESS8K, XPRESS16K and LZX (highest compression ratio).
There are also a large number of third-party applications for compressing files and saving space, but here we only covered the tools built into Windows 10.
 We are used to using our computer to conditionally divide the hard drive into two partitions: C and D, respectively. The system is installed on the first, and the user data is stored on the second. This is done so that the next time we install Windows, we can perform a clean installation and format the partition without losing user data. The article will discuss the question: how to partition a disk on Windows 10 and all the nuances associated with it.
We are used to using our computer to conditionally divide the hard drive into two partitions: C and D, respectively. The system is installed on the first, and the user data is stored on the second. This is done so that the next time we install Windows, we can perform a clean installation and format the partition without losing user data. The article will discuss the question: how to partition a disk on Windows 10 and all the nuances associated with it.
Very often there is a need not just to divide a physical disk into logical ones, but to change the size of existing parts - this will also be discussed below. It should be noted that it is possible to achieve a positive result using the system itself, but this will not be as easy as, for example, when using third-party software. For completeness, we will describe both methods.
The first option that we will talk about today is an already working system in which there is a need to split the disk into 2 partitions. You can complete the task without using third-party software. Let's get started.
- Right-click the Start button and select Disk Management.


You can launch the same tool in another way: simultaneously press two Win + R keys and enter the command diskmgmt.msc in the window that opens, and then click the “OK” button.


The upper part of the window displays a list of all disks and their partitions installed in the PC or laptop. Here you can see the file system type, size and status. In this case, physical disks are designated by numbers, and logical disks by the letters we are familiar with.
A partition map appears at the bottom of Disk Management. Thanks to rectangles, we can roughly estimate the ratio of partition sizes. In our case, we can see that the system partition is 500 MB in size, drive C is approximately 68 GB, and the user partition D takes up the rest of the space.


You cannot make any changes to drives that are missing letters. Most often, these are system-reserved areas that contain system or boot files. If you edit such a section, the system may become damaged or even permanently fail.
- We continue our instructions. In order to partition a disk, you first need to determine the free space. To do this, we compress the disk that needs to be divided. In our case, this is user section D. Right-click on it and select “Compress”.


- A small window will open in which we need to indicate how much the partition should be compressed. The space here is measured in megabytes, so we write 10,000 MB, which corresponds to 10 GB, and click “Compress”.


- The volume is being compressed. There is no progress bar here - we do not see how much is left until the operation is completed. The fact that the process is underway is indicated only by a circle of waiting. On our computer the compression took about 3 minutes.


- Now you can create a new partition. It is impossible to divide the Windows 10 system disk using standard means, so we will create an additional partition. How to increase the system volume will be discussed below. So, right-click on the unallocated space and select “Create simple volume”.


- In the volume creation wizard that appears, click “Next”.


- Specify the size that the new partition will receive and click “Next”. We will use all the space.


- The system will offer us a letter for the future volume - we agree and click “Next”.


- In the next step, you need to select the partition file system (we will use NTFS) and specify the volume name (it will be displayed in Explorer). When the necessary settings have been made, click “Next”.


This completes the volume setup. All we have to do is press the button labeled “Done”.






There is no need to squeeze the shrinkable disk to its limit. If you do not leave space on it, the section will not be able to fully function. It will not be possible to defragment, and the speed of the volume will drop critically, which will affect the performance of the entire system.
How to partition a disk during system installation
You can partition a physical disk with a clean installation of Windows 10. But then you will have to lose all the data. This option is suitable for those who bought a new computer or laptop and want to install the OS on it, or for those who have securely stored their files in another location. One way or another, let's proceed to the instructions for partitioning disks when installing the system.
- The process of installing Windows 10 is discussed in detail on our website. We are specifically interested in the moment of working with disks. Once the installation reaches the desired stage, you will see the following window.


- Let's say we need to increase the size of the first partition and reduce the second. Our disks are called “2” and “3”, you may have other names. All of them are located on physical device “0”. Let's start partitioning the disk. Initially, you need to delete both partitions. To do this, select each of them in turn and click “Delete”.


- As a result, we should end up with unallocated space. Select it and click on the “Create” button.


- Specify the size of the new logical disk and click “Apply”. We installed 40,000 MB, which is equal to 40 GB. You have the right to choose the volume you need - the figure given is only an example. For normal operation of Windows 10 you need to allocate 80 GB or more.


- The system will warn us that for proper operation it is necessary to create an additional partition. It will store drivers and other important Windows components. We agree and click “OK”.


- As a result, we received one system partition with a size of 500 MB, a disk for the system with the size that we specified (we have 40 GB), and unallocated space. This is what we will use to create a section for user data. Select free space and click on “Create”.


- Click the “Apply” button, thereby taking away all the remaining space for drive D.


- All that remains is to format the disks. We'll show you how to do this in the first section, and you'll do the same with the rest. Select the volume and click on “Format”.


- Windows will warn us that all data on the partition will be permanently deleted. Click “OK” to start the formatting process.


After a few seconds, the process will be completed and the drives will be formatted. Now you can proceed to installing the system. To do this, simply select the system drive (on which you planned to install the OS) and click the “Next” button.


We use third-party software
In addition to the standard system tools for disk partitioning, there are many third-party utilities that offer better functionality and ease of use. We have selected 3 leading programs and will describe in detail the sequence of actions with each of them.
Minitool Partition Wizard Free
This is a convenient application for working with hard drive partitions. All standard operations are also supported here: expansion, division, creation and deletion. There is a step-by-step wizard that will not let beginners get confused in the process.
You can download the utility. After the file is downloaded, proceed to the instructions for its use.
- Installing the utility is quite simple - first you need to accept the license.


- Select the directory in which our application will be installed and click “Next”.


- The program is being installed. When it is completed, all we have to do is click the “Finish” button.




Once the utility is installed, you can proceed to use it. Launch the program and follow the instructions.
- In the window that opens, click on the rectangle, which we have outlined with a red frame.


- Right-click on the desired drive and select the item that we indicated in the screenshot with the number “2”.


- Using the slider, change the size of the disk to the value by which it will be reduced. The rest will be cut off from the disk and will serve as a place to create a second partition.


- Click on the resulting free space with the right mouse button and select “Create”.


- Since we are going to create a new volume with the size of all the free space, we don’t change anything in the next window and just click “OK”.


- Apply the changes using the button indicated in the screenshot.


- Since we are working with drive D, a reboot is not needed. If the actions were carried out on the system partition, Windows would reboot.


As a result, the changes were applied and our disk was divided into parts of the size that we specified during the setup process. You can also merge disks in the same way.


Acronic Disk Director
This is a professional tool that can be downloaded on the program’s official website. The application is paid, but there is also a demo version. Let's look at the process of working with Acronic Disk Director:
- First, let's install the program. There is nothing complicated here. Once the file is downloaded, run it. Click on the entry indicated in the screenshot.


- We accept the license agreement by checking the box in the desired position and click “Next”.


- Select the directory in which the installation will be carried out.


- We wait until all files are copied.


- After the application starts, right-click on the name of the desired disk and select “Split Volume”.


- Use the slider to change the size of the two new partitions, and click “OK” when finished.


Starting with Vista and 7, the Windows operating system has a feature that allows you to shrink (or expand) the size of the main partition and logical drives. This feature can be useful if you find yourself in a situation where you need an additional partition and don't have enough additional disks. By shrinking the volume, you will free up disk space; this unallocated space can then be used to create other necessary partitions. Today we will learn how to shrink a basic volume or partition using the Windows GUI, and for more advanced users we will also describe a method using the command line.
Before you begin, make sure you have backed up all your important data.
Shrink a volume or partition using Disk Management
If you have Windows 7, go to the Start menu, type “disk management” in the search box and press Enter. If you are a Windows 8.x user, right-click in the lower left corner of the screen (or press Win+X) and select Disk Management.

"Disk Management" is where you will find all the drives connected to your computer (hard drives, USB drives, CD/DVDs, etc.)
Select the primary partition you want to compress, right-click on it and select Compress.
As a result, the operating system will begin the process of determining available space for compression.

Specify the amount of space you would like to regain and click "Compress". Remember that the amount of space is entered in megabytes: for example, 1 GB is equal to 1024 MB.

You can use the space freed (or unoccupied) in this way to create a new partition.
Shrink a volume or partition using the command line
To open Command Prompt in Windows 7, go to the Start menu, type "cmd", right-click cmd.exe in the search results and select "Run as administrator". In Windows 8.x, right-click in the lower left corner of the screen and select Command Prompt (Admin).
Enter diskpart and press Enter.

In the DISKPART line, enter list volume. This command will display a list of all drives on the computer.

Now enter the select volume command and the volume number you want to shrink. For example, enter select volume 1 and press Enter.

Enter shrink querymax and press Enter. This command will allow Windows to determine the maximum amount of space that can be compressed.

Now you have two options: first, you can simply enter shrink, and then Windows will shrink all available space; secondly, you can specify the desired volume to be compressed. In the second case, you need to enter the command shrink desired=volume_in_megabytes (for example, shrink desired=2048). You can enter any number that does not exceed the value specified in the "Maximum number of reused bytes" line. So with this command you can specify the exact amount of space to be compressed.

If you do everything correctly, after the operation is completed you will see a message:
DiskPart successfully shrunk the volume by: number_in_megabytes
That's all! To shut down DISKPART correctly, enter exit and press Enter.
Things to consider:
- When you try to shrink a primary partition or logical drive, you will not be able to shrink the partition beyond the area where non-movable files are located (for example, the shadow copy storage area, hibernation, page files, etc.) Let's assume if there is a "first" empty space on the Windows drive and then there are non-movable files followed by a "second" empty space, you will only be able to shrink the partition to the end of the second empty space since there are non-movable files in the middle.
- If a large number of bad clusters are detected, the compression will fail.
- You can use compression for primary partitions and logical drives or partitions with the NTFS file system.
Now I want to show you how you can use the unallocated space on your disk and create a new volume or partition using the Disk Management tool or using the Command Prompt.
How to create a new volume or partition through Disk Management
Open the Disk Management tool. To do this, open the Run dialog (Win + R), enter the command diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
Right-click on the unallocated space and click Create Simple Volume.
In the Create Simple Volume Wizard window, click Next.

Enter the amount of space you want to use for the new volume (or partition) and click Next.

In the next step, you can change the formatting options, but this is not necessary, especially if you are happy with the default settings. Additionally, you can change the volume label to any name you prefer, but it's better to use something descriptive: for example, "Movies", "Documents", "Backups", etc. You can also enable the option to compress files and folders. When all settings are selected, click Next.

Review your selections. If you want to change anything, click "Back" to return to the previous steps. If you are happy with everything, click "Done".

After this, a new partition should be successfully created on your computer.

How to create a new volume or partition via the command line
Open a command prompt with administrator rights.
Enter diskpart and press Enter.

In the DISKPART line, enter list disk. This command will list the drives on your PC. It will also help you determine the disk number with unallocated space.
Now enter the command select disk with the volume number and press Enter: for example, select volume 0 .


Advice: you can manually specify the size of the new partition. To do this, contact the team create partition primary need to add size=x(Where x– partition size in megabytes). The entire command will look like this: create partition primary size=1000
Now that the partition has been created, enter the command list volume and press Enter. As a result, you will see a volume (in my case volume 3) with a RAW file system. However, it would be more correct to say that this is a volume without a file system.

Next, you need to format the partition to the NTFS file system. Enter the command format fs=ntfs quick(Where quick– this is an indication that the quick formatting method should be used) and press Enter.

You have just successfully created and formatted a partition. The last thing to do is assign a drive letter to the new partition. This is also a fairly simple task.
Enter the command list volume, note the number of the new partition and enter the command select volume, not forgetting to indicate the section number. For example, in my case the command would look like this: select volume 3 .
Now you have two options to assign a drive letter: you can simply enter the command assign, but then the DiskPart tool will automatically assign one of the available letters to the new partition (this is what is shown in the screenshot below); or you can enter the command assign letter=f, Where f is the drive letter. If you choose the second option, make sure that the letter you want to assign is not already assigned to another drive.

That's all! Everything written above works in Vista, Windows 7 and 8.x.
contemplatorWindows 10 is a convenient and fast system on all types of devices, however, it is prohibitively heavy for the computer’s internal memory.
On some devices, especially low-end computers or tablets, Windows takes up too much disk space. The most common problem for tablets is a situation where constantly automatically downloaded OS updates clog up the memory so much that there is not enough space for regular programs.
There are many ways to solve this problem, comprehensive information about which we will provide below. Next, we’ll look at some of the most effective and convenient ones.
Let's start with the most complex ones, and then move on to the simple device configuration options provided in the OS.
This method is associated with deep configuration of the computer, but still does not require special manipulations with the system and is the simplest for freeing up a significant amount of information on the disk.

This tool is called "Compact OS" and its job is to "compress" system files, similar to the process of archiving data so that it takes up a lot of space.
The process for launching such compression is as follows:

The system will start compressing all files. This process may take about 20 minutes or more, depending on the amount of data on the system.
As a result, the volume occupied by the OS will be reduced by one and a half to two gigabytes.
Removing unnecessary files
An even easier and faster method, which is performed without additional tools. However, the size of the space occupied by the system will not decrease much.
You can delete unnecessary and intermediate data (temporary files) that have accumulated in the system over the entire period of use:
- In the main settings interface, launch the “System” icon, where all the settings for the operation of the OS are collected.

- In this system settings menu, you need to select “Storage” in the sidebar of the options sections, where, in fact, the files to be deleted are located. In this section, select the location “This computer”.

- Information about system memory usage and additional function buttons will appear. You need to scroll to the end of the page and click on the special “Temporary files” function button, which controls the storage of these now unnecessary elements.

- In this menu, you can view the properties of files stored in additional locations and clean your computer from them. Here you can delete temporary files by clicking the corresponding button at the top of the list.


Disk Cleanup
Find out effective disk cleaning methods in our new article -
This method involves the use of standard Windows self-cleaning tools built into the system itself by the developer.
You can clean the entire disk with the system as follows:
- First you need to open the properties of the “C” drive in the “This PC” menu in the “Explorer” system. This can be done by right-clicking the submenu and selecting the appropriate item at the very bottom of the list.

- The computer will launch a special small properties window for this disk. You need to go to the “General” tab (although the system often immediately opens a window at this point). Here, next to the disk capacity status chart, click on the “Disk Cleanup” button.

Here the system will not immediately launch the necessary tool. At this point, you need to wait a little while the computer indexes (collects information) unnecessary files that are not needed by the system, users or programs and are not used anywhere else.
- As a result, the Disk Cleanup window will open. Here in a small window you can select elements that can be deleted. Since these files are often not critical, it is advisable to mark all types. After this, you can click “OK” and start the cleaning process, or remove additional components.

- To free up more memory from system files, you need to click on the system file cleanup function button in the same window. The system will again conduct an “audit” and create another tab in the cleaning window – “Advanced”. Here, with one click, you can clean the system from its outdated rollback copies, as well as from unused programs.

Deleting the update cache
This method is the least dangerous for user data, since it clears the system from downloaded but not installed update packages, or from previous versions of software upgrades. If the necessary elements are deleted, the system can always be restored by simply downloading the previous update using standard tools.
The sequence of actions looks like this:
- The first steps are to turn off the System Update Center. Using the “Search” tool of the main panel, enter “services.msc” and launch the found configuration document.

- In the window that will immediately open by the system, find the “System Update Center” control option and open it by double-clicking.

- An additional window will be launched to configure the properties of a specific parameter. In the central tab, under the characteristics of the state of the current process, click on the “Stop” option, then confirm your action at the bottom of the window.

- Through the main folder of Explorer (“This PC”), open the following folders one by one: “Windows”, the main folder with the system and all files associated with it. “SoftwareDistribution”, a folder with settings and software for managing the capabilities of new system components. “Download” – a special download folder for downloaded software.

- In the download folder that opens, open the “File” item in the top panel, and in the submenu, among other debugging items, select the option to configure folder settings.

- After launching the parameters window, go to the “View” sub-item, and in the additional parameters field, set the status for hidden elements to “Show hidden files”. Also, to clear a larger amount of information, uncheck the box next to the option to hide special protected files.

- Then, select absolutely all downloaded update files in the folder and delete them, thus clearing all outdated, faulty and space-consuming update files.

- When the uninstallation process is completed, you must run the OS updater again for the system to function normally. To do this, reopen the properties window for this component (see previous paragraphs), and in the main “General” tab, under the status indicator, click “Run”.

Note! If the user wishes to no longer receive constant system updates in order to prevent the system from becoming overloaded in the future, this option can be left.
Video - How to reduce the size of Windows 10 on your hard drive
By default, most hard drives are accompanied by two volumes: C and D. These are the main partitions on the hard drive (volumes or root directories) that are strictly separated from each other. First of all, they are made so that the system does not have to wander in the wilds of heavy films and games on the way to vital files. For ordinary users, the ideal placement of programs, games and files: everything light and often launched - on the system drive (C by default), everything heavy and unimportant - on the second disk, an alternative OS - on the third. And in order to most efficiently distribute space between volumes or change their number, you should be able to manage disk space.
How to open hard drive management
Like most Windows Settings windows, Disk Management has many doors and can be accessed in many different ways. The simplest ones: right-click on the start menu and find the required item there (not available on all versions) or type in “Create and format partitions” in the search.
In Windows 10, “Hard Disk Management” is called “Creating and formatting hard disk partitions,” but in the window signature the name remains the same, and “Disk Space Management” is a completely different window with limited functionality.
If for some reason this method does not suit you, here is the path to disk management, which has not changed since XP:
- Right-click on Start and open Control Panel. If it is not there, you can find it through the search.
- Open the "System and Security" category when categorized.
- Scroll down and click “Create and format hard disk partitions”, under the “Administration” group.
You cannot access control via the command line. There is only a separate set of disk management commands as a fallback, but this is quite complex and pointless.
If it doesn't open
If the system does not allow you to manage disks, the issue is a limitation of user rights, since for this you need to have administrator rights. Most likely, the root cause of the problem is a virus on your computer and after following the instructions, be sure to scan everything and everyone with an antivirus.
Before proceeding with the method described below, try disabling your antivirus and try again.
- Search in the Start menu, find and open “regedit”.
- On the left side of the window, go to the path “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE/SYSTEM/CurrentControlSet/Control” and click once on the “Windows” folder contained there.
- On the right side of the window, open the “CSDVersion” option.
- Set the parameter to zero and confirm the changes.
Disk space management
So-called disks are correctly called partitions or volumes (you only have 1 disk, most likely), but given that even Windows calls them disks, this is not important.
To make one volume larger, you must first make another volume smaller. You can't just grab a spot out of nowhere and you have to find a donor first. It is worth saying that in Windows 10 there is no function for merging volumes. If you want to merge, you will have to use the standard methods described below and copying information from disk to disk.
There is one very important non-obvious rule that imposes a strong limitation on disk management, and before you start wasting space, you need to consider the most popular mistake.
Why is "Extend Volume" inactive?
Pay special attention to the order of the volumes in the lower half of the window.
In our case, the order is: C, J, D. After we pinch off a piece of space from one of the disks, it will appear behind the donor volume. For example, if we take a piece from drive J, the order will be: C, J, Free space, D. Free space can only be filled into adjacent partitions. That is: return to the donor volume (J) or expand the next disk (D). We cannot expand drive C, since there is an obstacle in the way in the form of drive J.
To expand the C drive, you need to completely remove J and make it a remote space. But if this doesn’t seem enough and you want to expand to include drive D, you’ll have to delete it too.
Expansion of the first volume is possible only with the help of an individual multi-pass or specialized programs.
For example, in this case, to expand drive C at the expense of D, you can do the following multi-step:
- Creating a new volume using drive D.
- Moves all files from drives J and D to a new volume.
- Removing the J drive and expanding the C drive using the freed up space.
- Removing drive D and expanding drive C using the freed up space.
- We call the new volume disk D.
- We move from C to D as much space as needed.
- We create drive J at the expense of C and move old files from drive D to it.
It all depends on the order of the disks, their volume and the availability of free space, so the multi-pass is individual.
If the disk with the system is not the first, then expanding the ones in front of it is impossible, since the disk with the system cannot be removed.
Compression
- Right-click on the partition you are interested in and select “Shrink Volume...”.
- Set the donor space size and click Shrink.
- Free space will appear behind the donor volume.
If you cannot compress the volume, you must either moderate your appetite or delete part of the contents of the volume.
Removal
- Right-click on the volume and select "Delete Volume...".
- All its contents will then be deleted.
- The freed space will appear in the place of the deleted volume.
Extension
The system disk expands just like all the others. But due to the error described above about the impossibility of expanding the volume, this is not easy to do. Before expanding your disk, be sure to read the first part of this chapter, which covers the most common disk management error.

Creation
Windows 10 does not recognize the difference between a local disk and a simple volume. In principle, there is no difference between them. The distinction between volumes and local disks was used on older operating systems and was purely a conditional limitation. By creating a simple volume, you create a full-fledged local disk.
- Right-click on the unallocated space and select Create Simple Volume.
- Select the size of the allocated space. You will not be able to use non-adjacent free space.
- Select a letter for the new volume.
- It is better to leave all settings as default.
- A new volume will appear in place of the used space.
Video: Disk Management in Windows 10
Defragmentation
The entire contents of the hard drive are divided into many small fragments, and when new information is entered, these fragments are located taking into account their best position for sequential reading, one might say side by side. However, when they change, new information is recorded and existing information is moved, a well-ordered structure gradually tends to become more chaotic. Moreover, bad sectors appear, where the reading process is greatly hindered. The process of optimizing this entire structure is called defragmentation and is recommended for periodic execution at least once every six months.
Checking the disk for errors is also included in the optimization process.
Defragmentation is intended exclusively for HDDs. For SSDs, it is not only dangerous, but also harmful. If you don't know what you have:
- HDD - The computer turns on for 10 seconds or longer, and the hard drive looks like a box with a round part.
- SSD - Windows starts in less than 7 seconds, and the drive looks like an electrical contraption, just like the other components.

Cleaning drive C
In addition to simply cleaning the desktop and deleting unused programs, it is worth getting rid of files that are actually called junk. Windows 10 has a very specific place for collecting junk and junk files - this is the Temp folder. Everything in it can be deleted without any regrets and the slightest risk of harming the system.
Cleaning the C drive through its properties in Explorer is less complete and does not affect some temporary files.
- Go to settings.
- Open the "Privacy" section.
- In the General tab, disable Ad ID and Start Tracking.
- Go to the Speech, Handwriting, and Text tab and turn off speech services if they are active.
- In the “Feedback and Diagnostics” tab, select the main method of data collection, disable the only switch and disable the generation of reviews.
- In the Background Applications tab, turn off the main switch.
Programs
As mentioned above, standard Windows tools for managing hard drive space are very limited in capabilities. If you are faced with an insurmountable problem or are simply too lazy to bother with moving space multiple times, you can always use the help of a special program that will do all the dirty and mental work for you in just a couple of buttons.

Proper distribution of disk space is a simple and very far-sighted action, and timely defragmentation is the key to order on your computer. You should only change the size of volumes or their number after carefully considering your future plans for using the computer and distributing priorities between heavy games and programs. The main thing is to always leave at least 10 GB of free space on each volume, especially on the system one, and do not forget about defragmentation.