In this article, you will find acquaintance with the Adobe Camera Raw module.
At first, what RAW is and with what it is eaten. To understand, briefly remember how the digital camera works (it does not matter, the digit or a professional mirror chamber, everything is completely the same anywhere). Light through the lens enters the photosensitive sensor, which consists of millions of sensitive elements. Initially, a black and white image is obtained, which is then divided into color pixels using peculiar lattices, called Bayer filters. At the output from the matrix, we have a RAW file (from English "raw"), which then with the help of special microcomputer algorithms, the camera is compressed, adjusted and converted to a well-known JPEG. At the same time, a significant part of the information is ruthlessly discarded.
Why are more and more people prefer shooting in RAW format? The answer is simple:
1.
No need to think about the settings of the camera (sharpness, saturation, contrast, etc.) - they always stand in the middle position.
2.
No need to adjust white balance. It can always be adjusted later with an accuracy of 1k, or at any neutral point, and without loss of quality.
3.
If you are mistaken with the choice of exposure, you can adjust it later without loss of quality, and up to 4 steps, which is absolutely impossible to do with JPEG files.
4.
From RAW easy to make JPEG or TIFF files of any quality, while you will have the original. Therefore, RAW files are often called digital negatives. The initial color depth ranges from 12 to 16 bits, against 8 in JPEG, so it is easy to restore information in lights or deep shadows.
5.
In JPEG, each subsequent file transformation leads to loss of information, that is, the deterioration of quality. The RAW does not happen.
The disadvantage of the format is a large amount of file (about 2-3 times more than a similar JPEG file).
Briefly go through the module interface. For example, I took Adobe Camera RAW 4.6 for the Russian version of Adobe Photoshop CS3. The module consists of 8 tabs, whose switching buttons are shown in number 1.
The first tab presents the main adjustments (2).
The top line shows the tools icons in which it will be easy to deal with those who already know Ase Adobe Photoshop (Without it, you should not start acquaintance withCamera.Raw). When you hover on them, the mouse cursor appears pop-up tips. By clicking on the bottom line (3) you can open the Color Profile Settings dialog box and the resolution of the original image.
The second tab is represented by the master curve of the RGB composite channel
Customize (on the professional jargon "bending") the curve can either sliders (parametric curve) or by setting and moving control points (point)
On the third tab, the sharpness of the image is adjusted, and you can also reduce the color and monochromatic noise. To observe changes in the image, you need to increase the size of up to 100%
The fourth tab provides great color management capabilities, the adjustment is much more accurate and more diverse than in Adobe Photoshop. You can make a fine setting of saturation, brightness, shift certain colors on the color scale. Also, if desired, you can seek a wide variety of fantastic effects, cross-processing effects.
Here you can make a mixture of color components in grayscale grades, that is, to translate the snapshot into black and white.
The fifth tab will help to eliminate extraneous shades in shadows or lights, if the shooting was carried out in difficult lighting conditions, and the color balance in the lights and shades is different. Here you can also achieve certain effects.
The sixth tab serves to eliminate chromatic aberrations (the appearance of colored oles around bright objects) and the effect of vignette when shooting with a flash.
Using the following tab, you can create your own camera profiles for different shooting conditions.
On the last tab, you can select the profile you created, the settings of which will be applied to the image.
Those who wish to thoroughly study the Camera Raw module can do this using the appropriate special literature, as a detailed description of all functions and settings takes the book of a decent format.
Step 1.Open the file in Adobe Photoshop. This automatically starts the Camera RAW module.
Analyze the image to submit a plan for further action. We need:
1.
Change white balance towards warmer tones. Usually the eye is better perceived warm tones than cold.
2.
Configure exposure.
3.
Show details in the dark areas of the image.
4.
Make the colors of the image more saturated and diverse. In this case, we will use the Adobe Photoshop program and the Lab color space to which there are no equal in the expansion of the color range.
5.
Remove unnecessary noise and enhance sharpness. Here we will also turn to Photoshop, since the arsenal of his methods in this matter is much richer.
In this direction and we will work.
Step 2.White balance setting.
It is done easier than simple - we move slightly slider Temperaturein the direction of the yellow spectrum area.
In each case, it is necessary to do individually, sometimes everything comes down to the only mouse click on the neutral area, but in most cases you have to regulate two sliders. Reaches a little, you will understand how easy it is.
Step 3.Customize exposure. Everything is also very simple - move the corresponding slider to the right to increase the exposure, to the left - to reduce.
Step 4.We show details in darkened areas. To do this, move the parameter slider Filling light Slightly right
Step 5. Now let's open our image in Adobe Photoshop. To do this, just click on the button " Open image. "Our file will open in a familiar program.
I translate the image to LAB mode: Image - Lab mode - Lab (Image - Lab).
Create a corrective layer Curves (Curves). Apply the desired form of curves, in each case it will be individual, in this case I got the curves shown in the drawings.
The advantage of the correction layer is that you can change the shape of the curves at any time, the layer opacity, its overlay mode, apply styles. Here is the result of the use of curves.
Now we drain the layers by clicking SHIFT +.CRTL +.E..
Step 6. We remove the noise and increase the sharpness of the image. I will not stop in detail on these operations, as the site has many lessons on these topics.
I wish you easy and pleasant work in the Adobe Photoshop program!
I asked me many times to write starting photographers about the processing of RAW files, but I thought about it already a lot is written by other authors, and then I once again asked a good person, so I share my knowledge and experience.
Raw file.
If you are still shooting in Jpg., then know that this is a miserable similarity Raw. File in terms of extracting features useful for photographer information. Raw. The file is essentially almost raw data that has not passed (should not at least) processing the balance of white, correction, and other things. IN Raw. The file is better "pulling" shadows and better compensate for the overexposition. It is precisely why it is best to shoot in Raw, and no additional jeep on the memory card not to write.:
1. You can always make it from Raw.
2. He takes place
3. It slows down the surveillance buffer in the chamber when recording on the memory card (written not one Raw., and jeep)
Although Raw. The file is essentially raw data, it is not so simple when you open it in the RAW converter. He goes "with a trailer." A profile of distortion correction, vignetting and noise suppression profile is often embedded. Probably, the recorder of such small "fraud" can be considered SonyFor the files of which it started to work noise from certain ISO values. Followed by her Fujifilm. And aggravated the situation. You open the RAW file in Adobe Camera Raw. (hereinafter ACR), and there is no longer distortion and vignetting, and often noises are "crushed". This is probably good for a novice photographer who does not want to learn photos, but wants "Clazz Claz" and bad for the one who is trying to figure out which ISO is better to shoot and what characteristics of his lens.
Raw converters
Raw Converter This is the program that decrypts (I write simple words) The initial data correctly and shows us visually, as a picture.
In fact, it is possible to decipher data differently and therefore the result is slightly different from different RAW converters. The most famous and most "advanced" is, of course, Adobe Camera Raw.. He understands DCP color profiles, has many means of monitoring perspective, distortion, vignetting, flower changes and work with noise and sharpness. Promotes the Giant Graphic Market - Company AdobeSo you want - you do not want, and everyone else has one way or another to navigate it.
Here, everyone who uses another RAW converter (from experienced photographers) will be indignant, remembering his undeservedly "forgotten" Capture One. or RPP.but the fact is a fact - Acr more powerful, easier and develops faster.
Nevertheless, this favorite of RAW converters is not so ideal. An important point he is that he uses all these "inconsistencies", which the camera manufacturer firm hangs up to its RAW file format and includes them without notifying the user and turning off. To understand how it happens you can see. IN Acr No noise and everything is somehow smooth. But it is worth opening in another RAW converter and it turns out that there are really a lot of noise. In fact, when you open the file of this chamber in ACR, automatic noise reduction, correction of distortion and vignetting. Software itself.
Why, for example, like 90% of the other photographers, I use Adobe Camera Raw? The answer is simple - this program has a big corporation and will develop further, while others, including very promising RAW converters, hold on one person. When he gets bored, he will just throw a project and you will stay without your favorite tool. Because let's talk about opportunities Adobe Camera Raw..
Adobe Camera Raw Opportunities
I use the standard photo cataloging agent, Adobe Bridge.. It is closer to me on ideology. This is a full-fledged agent only to flip, put the assessments of the photographs, watch the shooting parameters, etc. Nothing extra. For those who want "Combine" exists Adobe Lightroomwho also uses Acrbut ideology there from stream photography.
First, immediately update your Acr to the current version. It is updated quite often and some functions that were not in old versions appear.
As you can see, there are three important elements of the process of manifests RAW:
1. Main panel
2. Auxiliary panel
3. Histogram
Basic Parameters / Basic

White balance
The first thing we do is put the white balance. Well, if we know it, the camera guess him or we used the color scale.


Select the gray pipette and click on the gray patch, the third left. This is a medium-gray neutral color. So we will have the most accurate white balance.
If the scale in the test frame was not, then use the standard settings in the White Balance menu or send the White Balance Slide while you do not start like the skin color model. Also in the frame there may be something neutral gray, to which you can poke the pipette, assuming it is gray. Such a help from time to time is found.
For example, in the frame where the girl sits on the sofa for her back the perfect "gray card" of gray and black stripes. But note that objects that at first glance may seem gray, in fact it can easily have a bluish or beige shade and then you will not be able to use them as a calibration element.
bar graph
Now you need to make sure that the indicators of the overestpring and no-exposure are included. To do this, check that small triangles are included on the histogram (circled by the square), as an example.

Now, if a snapshot is incorrectly exhibited or too contrasting, the overexposed areas will be highlighted in red, and unplanned blue.

Places selected blue have a color value: 0, 0, 0

Places highlighted red have a color value: 255, 255, 255
You need to avoid both cases, if only it is not a catalog of shooting, where the background should be pure white or black.
Exposition
If you have a small overall error in plus or in minus, then use the "" slider.

Contrast
Sometimes it is useful to increase the contrast photo to get a brighter color. This is the most effective way to improve the photo without spoiling it (if you increase the contrast in reasonable limits).
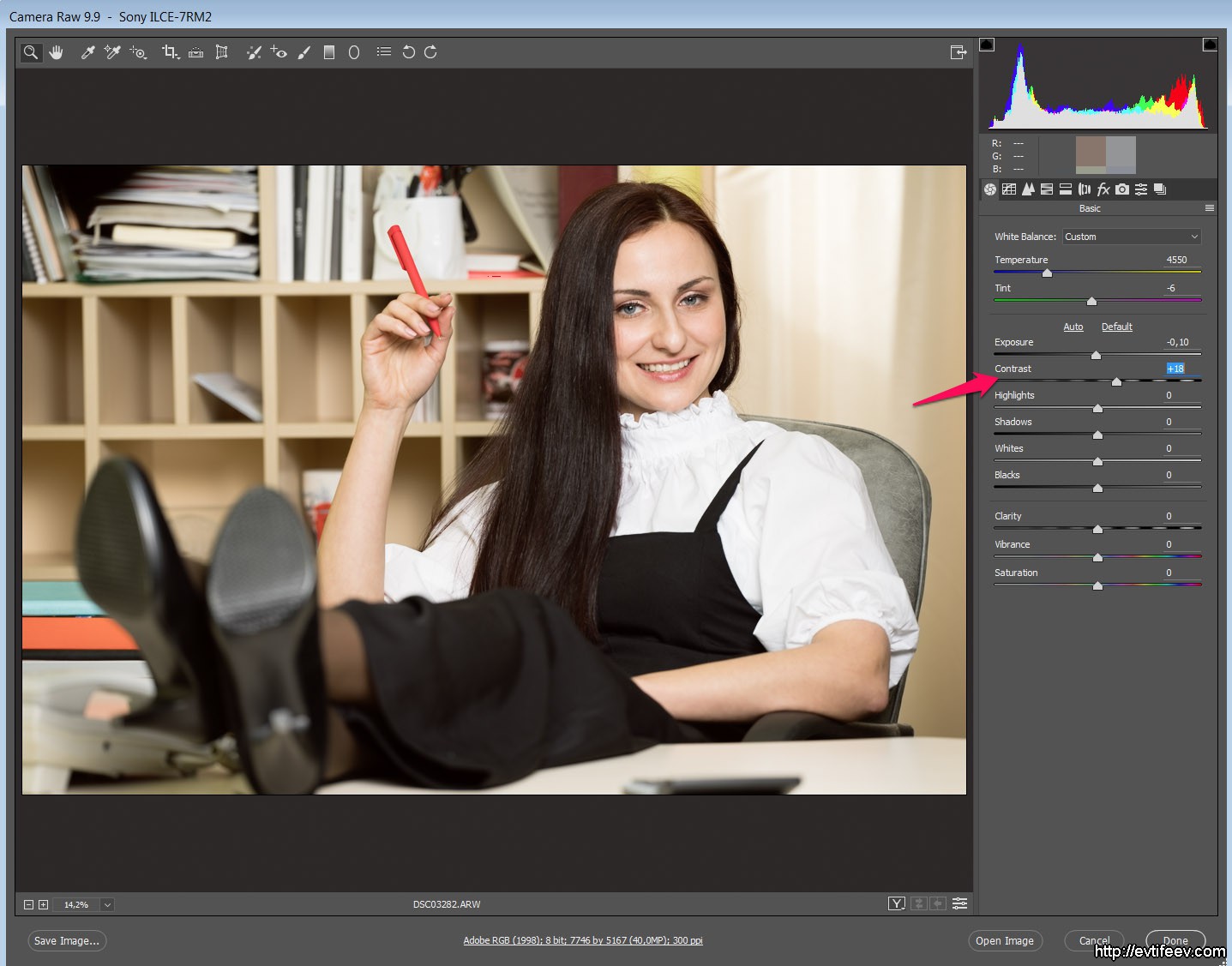
"Sveta"
"Light" is not white. But close. And you can brighten them to white or darken to gray.

In this photo, the main "lights" accumulated on a white shirt and the "mouse", which lies on the table.
They could go to the "Peresvet", but the exposition here is ideal and therefore they are exactly how should be on the verge.
"Shadows"
"Shadows" is the whole jumpsuit, stripes on the wall, under the sofa, etc. There are a lot of shadows in this picture and they define an excellent contrast with a light wall and a white shirt.

Shadows could have been lazy to this slider, but I spell to use you. The shadow lives a terrible beast - "noises." Any frame area, where little light fell, is a potential source of "noise." Many novice photographers believe that there should be absolutely everything in the photo. This is not true. "Everything is seen" is tantamount to "nothing can be seen." The snapshot should be a story accent and insignificant areas. These are insignificant and must go into the shadow, setting the total contrast compared to the bright main character of the picture.
If you are having a shadow, then pull out "noises" from there and after you have a crazy task to destroy the monster you yourself created.
I have a relatively new Canon 5DSR camera, so the shadows stretch well and no noise. I had to raise the exposition on 2 steps to see them.

Here are these green and purple points - "noises". You do not need to fight with them, you need to avoid competent shooting and competent processing. And if without it nowhere, then we will reach the "Noidav" tab.
"White"
"White" slider is needed much more often than the "shadow" slider. Often allows easy motion to avoid overexpose in the frame, if it is not critical.

As far as you can "pull out" a snapshot from the local overexpose depends on your camera. Modern cameras at least improved their figures in this regard in about 2008, but still not aspressing is not so scary compared to overexposure. Simply put "Peresvet" it is almost always the impossibility of saving the photo, there is little stock there. But if I have little shine, but pull something, albeit with noise and dirty flowers. This applies to all cameras, do not think that you have some kind of special. I tried the newest and Sony A7R II.. Miracles does not happen :)
"The black"
Sometimes you need to increase the contrast of the object, which has white areas. The contrast we raise the flashing white and darker black. If we can not touch the white, then black. That is what this slider exists. You can also remove the black from all over the frame, but I can not imagine when it can be needed throughout the frame, except that locally, but this slider acts throughout the frame.

When you run this slider, make sure that you have an incompression indicator on the histogram. This will avoid "knocking out" in black areas that you would not want to see an absolutely black spot.
Microcontrastructure / Clarity.
Microcontrastructure behaves roughly as a rough increase in sharpness. Sharpness, it, of course, does not add, but adds the illusion of sharpness.

Use very carefully or do not use at all. There are much more gentle methods for enhancing visual sharpness, including in the process of the RAW manifests (do it before).
Nuclear Color / Vibrance
Literal translation - resonance. I call it "nuclear color" because it just urges all colors. After such a strengthening of colors to look at them is simply impossible.

Most often, lovers of this slider "pierced" on objects, to the color of which our eyes are especially sensitive: the sky and grass. You know all the colors of the sky, if you are not a permanent resident of the subway. The same with grass. Error in the grasses color is very easily recognized. The wrong color of grass and heaven is rejected by most viewers. Forget this slider!
Instead, the slider use the "contrast" and another tab that is called HSL / GRAYSCALE (Next).
Color saturation
The influence of this slider is practically the same destructive as the previous one. In fact, all three last sliders are harmful.

Harmful, because they give the appearance of easy achievement of the result and the novice thinks that everything is ok. And in fact, he spoils his best in its original photo of bad processing. It would be better not to do anything then.
If your color snapshot is too flexible, then you usually have reasons that led to this during the shooting process. Take what this picture is marriage. Set the reasons for such a marriage and in the future try to shoot better. You do not need to take a piece of town and try to squeeze out of it what is not in it. To get a great picture you need to first make at least a good picture, and then it is high quality and minimally to process it. It does not mean repaint it completely! As a rule, all processing is to remove dust, increase the contrast and correct some small geometric defects. Everything! You are a photographer, not a retoucher. Leave retouching professionals.
Alignment and clipping snapshot
Here I will have to make a slight digression from the "main panel" and spread to auxiliary. The fact is that after the alignment of small flams in the photo I want to align the horizon. Those. Neither a man nor the horizon on the landscape photo should not be rented on some side. But some pictures always turn out with a slope, especially when passionate about the plot.
In this case, I was lucky and on the wall there are vertical lines. The high probability that their adhesives are exactly vertically and the wall is smooth.
I will choose the "line" tool, click in any place line, which should be vertical and stretched down or up.

The picture will turn a little, by correcting your position and you will see the line of the alleged circumcision of the photo. On this line, you will also see the control elements - small squares for which you can pull and shift the cut line.

Control boxes are marked with red arrows.
In this case, I do not like the second layer of the curtains at the top, I will go down the cut line. I also move the left line to the right to cut off the wire on the floor and some box. It would be possible to restore the floor in this place if I really needed a whole snapshot, but this is not the work for novice photographers and therefore it does not apply to the topic.

I press ENTER and excess from the snapshot is cut off. In fact, nothing was physically cut because We work with the RAW file, but in the XMP file that is now attached to the RAW with our settings changed. Now the snapshot will open like this ...

If we leave the RAW file now by clicking "Finish", then later we can always return and cancel the crop by selecting the Crop tool (specified by the red arrow) and pressing the ESC.

If you need to align the snapshot, then you can always just trim the snapshot to the desired proportion using the Crop tool at once.
Now with a calm conscience we return to the "main panel".
Second Tab - Tone Curve
This tab allows you to work with Adobe Photoshop tool called "Curves". This is a very flexible tool and it's great that you can use it before entering the Photoshop itself, because It is not destructive. You can always cancel these changes. And changes with the help of "curves" can be very global. There is both just clarifying the darkening of pixels of certain brightness and work in color channels.

If in the Basic tab we did not have settings for "lights", "shadows", "white" and "black", then there are special control elements here, which limit the action of the slider. Which range of brightness to be considered shadows, and what lights? You yourself are determined by the points specified in the picture with the Red Arrows.
If you do not change the standard settings, then the "Light" sliders, "shadows" and so on., Which I lined up into the Red Frame will work in exactly as on the first tab.
I specifically displaced control points and in the area of \u200b\u200bthe collapsed mug, it can be seen that the range of lights on which I was influenced quite small.
There is also the second tab called Point. It gives the most flexible curve setting. There is nothing difficult here, but be careful when working with the curve. Most often, the light and shadow are still distributed more or less normal, so that if you drag the light into white, you can lose color, and from the shadows can be pulled out "noises". At the same time, such a curve can be very useful, for example, when processing underwater photos, where the red canal is usually completely bad. You can create yourself a setup-profile that will weaken green blue and strengthen red and apply to all photos. Plus it is again not destructive reception, your settings are stored in a separate file.

Large Arrow, I marked the drop-down list where you can choose the standard "linear contrast" settings (default, the linear curve), the "mid-contrast" and "strong contrast".
You can switch linear-medium-strong to understand how they are achieved. The curve becomes a sinusoid, dimming shadow and lightening light.

Based on this knowledge you can decide what you will dry or dim. You need to do it for all channels or for some one.

The list of simple features does not include this feature (especially when working with individual color channels), so if you do not understand something, do not be mistaken, you will understand it later when it really needs.
Detailing tab
The Detailed tab is responsible for the visual increase in the sharpness of the photo and for the ill-fated "noise".

Enhance sharpness
The first menu with red arrows is a visual increase in sharpness. Obviously, we can not take an additional detail of the snapshot from nowhere, but we can always make the viewer's brain think that the photo is clearer than it is. For this purpose, a long known (but not less surprising) method of processing image contours is used (the method is also called in the Russian contour sharpness), where the contour itself is darkened and dried with a white line from two sides (if you say simple words again).

With the power of the effect, everything is clear, the more - the stronger the effect of increasing visual sharpness. There is a threshold at which artifacts begin to get out. Try not to overdo it in the strength of the effect, it is better to find the correct radius for your size of the photo and the size of the parts and then increase the effect strength.
The "Minor Details" menu item allows you to enhance the textures in the photo, and the small values \u200b\u200bof this parameter make it possible to work only on edges.

The "mask" point allows you to focus on sharp contours, applying a method of increasing to them. It is worth paying attention to the fact that all menu items have a visual mode if you hold the Alt key and move the slider.

Noise suppression
I evil the shadows using the shadow slider from the first tab and my noise appears here where there were shadows. I start with the analysis of these noise. The fact is that noises are divided into two types: brightness and colored. Brightness are points of different brightness, chaotic allocated throughout the picture. With them, nothing can be done with them, just blur a little snapshot. The snapshot will be less sharp, but the points will be less visible. Brightness noise is characteristic of very high ISO when shooting.
Color noises are always present in the shadows on any ISO. They are manifested when you brighten the shadows. They look with colored violet, green and red dots located in chaotic order.

Accordingly, the arrows are labeled sliders, which allow you to fight with different types of noise.
Now we are discussing only the work in Raw. converter, but you should know that except Raw. The converter is another mass of ways to fight "noises."
There are plugins for Adobe Photoshop., eg, ImageNomic Noiseware. or TOPAZ DENOISE.. Both are considered good options in the suppression of noise when you have a difficult case.
There is also a technique MultiShotwhich helps when shooting from a tripod. You make a series of pictures on high ISO (for example, shoot the starry on the sky on the short exposure because the long star is already turning into tracks), then fold the pictures and only fixed objects remain in the pictures. The noise is chaotic, because they are deducted from the snapshot. I think it will be important for you to know that there is such a method.
HSL / GRAYScale
Tab HSL / GRAYScale Manages colors bands. HSL is a color description model and decrypt as HUE / SATURATION / LIGHTNESS (color / saturation / brightness). This model can describe any color.
You can choose a range of colors and change the color, color saturation and brightness. It is very effective and when used by using a neat agent.
HUE (Color)

The last two lines put me in the difficulty in translating the color. Both of these colors in Russian purple :) But in English purples are divided into three types.
Thus, dragging, for example, the red slider to the right, I get not brown, and the red table.

Please note that when repainting a rather narrow range of colors is captured, the floor remained brown. This happened because the computer knows the floor only seems brown, and in fact he is closer to orange. If you touch the orange slider, the floor will immediately begin to repaint. In any case, all the colors of the snapshot are in one of the ranges from this list.
SATURATION (saturation)

Here you can strengthen any color. In this case, I pulled the red slider and even the lips shone the new makeup.
Lightness (brightness)
Changing the brightness of a small color range can be achieved good results. I spent this tab from time to time to make a light blue sky darker without affecting its color. You can make it darker and reduce saturation. It turns out similar to the real color of the sky.

I recommend not to raise saturation, but only to reduce it when you need. Also useful when Adobe Camera Raw. incorrectly handles red. You can reduce saturation and get a softer skin color.

In this case, I darkened orange colors by making a girl tanned.
Split Toning
Tab Split Toning It is literally translated as "separate tinting" and the essence of it in painting the light into one colors, and the shadows to others. For example, light in warm, and the shadows in the cold. This tool is not introduced by accident and why it works can be understood from the article in its part.
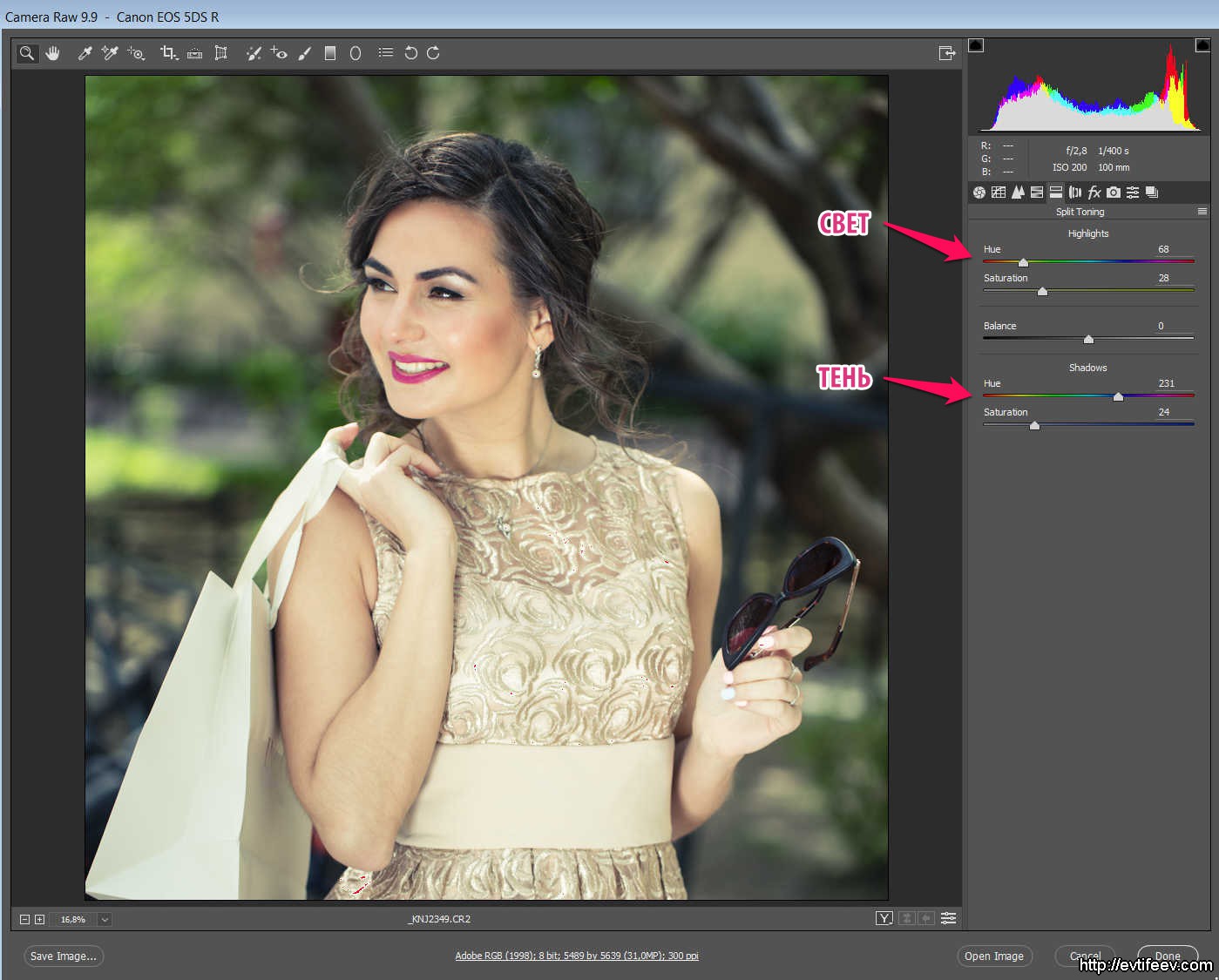
Using the color slider, we change the color of lights or shadows to the desired. Typically, warm tinting is used for lights, and for shadows is cold. Then you choose the saturation of this toning slider "SATURATION". Between the adjustment of the tinting of lights and the shadows is the balance slider between these actions, i.e. What actually consider lights and shadows.
Example

Your taste, of course, you need a snapshot toning or not needed. Sometimes toning saves a mediocre picture and this very often uses photographers who remove the weddings.
To cancel the effect of a sufficient saturation slider (saturation) to put in zero.
Lens Corrections
This tab is designed to eliminate the effect of the imperfection of the lens to the snapshot. On this fragment you can see if it is strongly closed in the form of purple cuts on white vertical elements.

Here you see the items of automatic fixing the effect of a particular lens in the Profile tab.
Remove Chromatic ABERRATION - removal of chromatic aberration.
Enable Profile Corrections - Corrections of the effect of the imperfections of the lens with the help of the profile (correction, distortion and vignetting)
In the drop-down list, there are a lot of photo lenses of all brands.

You can include corrections separately, as well as manually adjust the distortion (initial value of 100%) and vignetting (source value \u003d 0) sliders just below, if you enable automatic correction using the profile.

Additional corrections of distortion and vignetting are shown in red arrows.
Effects - FX.
Next tab Effects. Accordingly refers to special effects.

We offer three types of effects:
Dehaze. - Elimination of smoke
Grain. - grain
POST CROP VIGNETTING —
The effect of dehaze you now see the picture in the form of high contrast and increased saturation of colors.
Influence Grain. (grain) It looks like a natural film grain. It can help create the visibility of a film snapshot.

With the help of additional vignetting, you can add an emphasis on the center of the picture, it is useful for not very successful portraits. In any case, this is another tool for adding a visual scope (a large bright spot against the background of a darker environment attracts the viewer's view).

The vignetting function has many settings, but I will not stop at all.
Most of them: Vignetting force (Amount), removal from the edges (midpoint), Roundness (roundness), Feather (Rastuchevka)
Camera Calibration
A color profile for the camera is installed here.

Top tab Process. shows us that style work with color Adobe Camera Raw. Three times changed, so if you suddenly open your old files, you can detect an exclamation mark in the triangle in the lower right corner. This means that the old process was used and if you click on this label, the process of working with the color will be updated and the snapshot will slightly change its appearance.
Next you see the menu Camera Profile. The fact is that the chamber can be calibrated in relation to color reproduction. For this you need a color scale, like X-Rite ColorChecker. "Canon Krasit", and Nikon Sinit remained in the past. In addition, you can connect your own profiles for special needs. For example, I connected the color profile for infrared shooting, which allows me to clean my infrared pictures without limitation in color temperatures.

Presets.
Tab Presets. (Settings) contains a list of your white balance settings, cropping, contrast settings, and sharpness, etc. from past photo sessions.


The red arrow indicates how to get into the menu to save, load or use presets.
Menu Saving Settings Picture Looks like this ...

A wide selection of the fact that you want to save from the settings, but what is not.
Snapshots - Snapshots Settings
In the process of manifestation settings, you can find some good solutions, save them and then continue experiments with the ability to return to the saved settings. This tab is just implementing this feature. Adjust the snapshot as you like, then click on the "new" (specified in the red arrow) and set the name to your settings.

After that, you can change the current settings as you please. When you get tired and you decide that the old settings were better, you go to this tab, click on the name of the settings snapshot and your picture is miraculously returns to the previous view.
Auxiliary panel
The top panel I called the auxiliary because She has to enjoy less often, in the picture it is in a red rectangle.

In this panels are concentrated in essence tools, although in the last edition to it moved some more complex elements.
Lupa

Pro Lupa There is nothing to talk particularly. Increases and reduces the snapshot fragment. You can do the same using the Ctrl + + "+" / Ctrl + "-" keys (for the poppy use CMD instead of Ctrl).
Hand

Tool Hand Allows you to drag the image fragment on the screen if the image is larger than the active window.
White Balance Tool / White Balance
Color Sampler Tool.

In the picture you see three "sights" in different places. And an informational place where color values \u200b\u200bfor these three points are shown in the image.

As a rule, in the image you need to put several checkpoints to track changes in important places when you work with color, illumination or contrast of the image. This option is for relatively advanced photographers / retouches and allows you to stop while improving the image in the process of "Manics".
Targeted Adjustment Tool

Tool Targeted Adjustment Tool Allows you to influence the image using tabs. Tone Curve. and HSL / GRAYScale. In my opinion, not too useful tab, in the same way you can use these tools through the main menu.

In this tool, you can choose the aspect ratio of the future fragment and "enable" the grid.
TRANSFORM TOOL
Very useful tool that I first discovered in the RAW converter Capture One.. It allows you to correct the image geometry, where there are straight lines of the arrangement of these lines in the correct position.

This snapshot has straight lines to the left and right on which you can see the geometric distortion of the picture and orient on them can be distorted. This happened from the fact that I bowed a slight-angle lens slightly. Vertical lines began to diverge up. If I raised the lens up, then they, on the contrary, would be to converge. An ordinary lens is often useful to raise up, then lower down. Not always the field of view of the lens captures what you need. Only drivecase cameras can change the composition without lens slopes. I already wrote about the lenses, and we will talk about cardan chambers in the following articles (in very short time).
I designated red rectangles guides that I simply put along these direct lines that should be vertical. The program itself understands where the lines should be vertical, and where horizontal (evaluates the angle of inclination), so you just need to put the guide and snapshot in the right place.

Another example.

Old pictures, until 1925. Approximately, please us with the correct geometry. Why is that? Yes, because until this point, all photographers were filmed to drive cameras, which gave the opportunity to correct the geometry of the picture. It is easy to see the architecture pictures, the walls of the buildings along the edge of the frame are always parallel to the edge of the picture.

Parade Leib Guard Equestrian Shelf

photo: Karl Bulla, famous St. Petersburg Photographer of the beginning of the 20th century.
The inner view of the passage of St. Petersburg. 1900.
It would seem why other cameras came up with if the drives were so perfect? For a simple reason - they are very heavy.

karl Bulla himself.
Removed with such cameras almost exclusively from the tripod. Transferred only on the cart, on the horse, and later by car.

On the roof of the car with its cardan chamber stands Ansel Adams. Another legend of the photo, with the creative of which I highly recommend getting acquainted if you have not done this yet.
In 1923, Mr. Oscar Barnak, imagining with the then cameras in his mountain walks, invented the camera, which later began to be called Leica I.. From now on, it is possible to start counting pictures with distorted geometry :)
But it became possible to climb from the camera even to Everest than some and took advantage of (some, however, stayed there with the camera).

This snapshot is made on Zeiss Distagon 15 / 2.8. A very wide-angle lens that, when the lens is tilted down (to capture the track in the frame), tilts the walls to the center.
I allocated a red square to the tool TRANSFORM TOOL. In this menu there are simple perspective controls and if I were exactly in the center, it would be perfectly straightened the walls with one hand movement, the top point of this menu (in the frame).

I stood a little right of the center of the corridor, so the right wall leaned stronger (when correcting the right wall, the left leaned in the other direction) and specifically for this image preferably use the guides, as in the previous case. But if it were in the center, it would be corrected one step.

result correction of geometry
Another example is a picture of the building in front, if I do not stand in the center of the building. In fact, in the case of a wide-angle lens and disappear of special tools for checking the position of the camera, it is difficult to get up exactly in the center, and sometimes it is impossible when there are some obstacles in the form of other houses, pillars, and so on.

By a snapshot, I see that the left part of the buildings is more right, then I stood to the left of the center of the object of shooting (two buildings). To correct the geometric distortion, I use the second menu item.

The prospect was corrected by the price of a substantial piece of frame. But nevertheless, for amateur filming, this is a good way to make an acceptable frame.
The rest of the tools will not comment in such detail. They are too simple:
ROTATE - Rotate the picture, allows you to align the horizon line. We also did the most careful "ruler."
Aspect - corrects the aspect ratio (has never used for real frames).
Scale - Scale of the snapshot (has never used for real frames).
Offset X, Offset Y - Offset over the axes (has never used for real frames).
Spot Removal
Pain removal tool. It is convenient because its action will continue even if you open the RAW file later and change the settings of the exposure, contrast or any other image of the image. You can also remove this stain correction, this action is not destructive.

On the right there are settings for Spot Removalwhich include the size of the brush, the degree of decisive brushes and the opacity of the brush.
Understanding the right settings will come with experience quickly.
Red Eye Removal
Tool Red Eye RemovalAs follows from the name, it serves to remove the red spots in the eye, which is formed due to the illumination of the pupil portrayed by the flash "in the forehead".

In the left menu, you can choose the size of the pupil and the degree of dimming.
The red pupil is selected by the stretching frame, the program itself finds a red stain and discolor it. It works quite efficiently. Show me nothing because "In the forehead" I am not a candle "naked" flash and you do not advise you. Most often it happens when you take off on a smartphone or "soapy", where the flash is built.
Adjustment Brush.
Adjustment Brush. - Very useful tool!
Allows you to make all adjustments locally, i.e. Only in those places where they are needed. All may include all: exposure, white level, black, contrast level, microcontrastructure and a bunch of other settings.

Suppose you photographed the liner. The lights are burning on the liner and they, they yourself, knock on white and yellow glare on the night landscape. It is not always good, because Around a large glare there is still the so-called "Halo", i.e. Glowing circle.
At this picture, knocked in white light is shown in red. We will "eliminate".

I took Adjustment Brush. And drawing everything that you see purple (mask showing your actions with a brush can be turned on and off the checkbox below in the menu). In fact, I put the White in -6 and passed the brush on the lanterns and glare from them. In the real snapshot of the perspirations will be less if they are not broken at all, Adobe Camera Raw. There is a stock, safe white shift in a plus when manifest that you can use the restoration of lights.

Result
Let's try to enlarge the microcontrast locally.

source image
Here we see not too contrasting, but with the potential to increase contrast. He has colored facets, white and dark gray facets. We will relieve the brush of the overgrown and improve the microcontrast.

Drew a stone to raise the microcontrast.

Rose microcontrastructure and removed the rebar.

As a result, something is obtained. This is a very fast snapshot and very fast processing (only I took a frame on black, where dust is less visible).
Graduated Filter.
Suppose you went to the photo copying without your favorite gradient filter, which allows you to level the light of the earth and the sky. And here is such a landscape ...

All is well, but the sky is too light. And then a gradient filter comes to revenue from Adobe Camera Raw.. First you need to expose the exposition in minus (how much you need - try experimentally), and then stretch the gradient from top to bottom. So that he ricked out strictly down, hold the Shift key.

Accordingly, the gradient may consist of completely different effects, any of those specified in the right menu. For example, it can be color.

conventional gradient

Radial Filter.
The last of the filters under consideration will be Radial Filter.. It allows you to apply all the image parameters in the form of a circle or oval. Sometimes it happens convenient to highlight the composition of the composition.

Menu of the auxiliary panel - "Secret Functions"
We put, we decided to remove something very long or high. This will help us create a panorama. We make a few snapshots, turning the camera on the "panoramic" head, on a real panoramic head (where the lens is fixed in a nodal point) or with the help of a tilt-shift of the lens. At the exit we have several frames with a displacement.

Open these files in Adobe Camera Raw..

On the left above there is a small button, when you click on which we will see a small menu. In the screenshot it is already open.
The menu offers us three functions:
1. Synchronization of shots by the manifest parameters (it is very useful for a photo series)
2. Creating an HDR picture (we will not stop on this function because Photoshop it realizes badly)
3. Creating a panorama (this photoshop does well)
Creation of panorama
Select three snapshot using Ctrl + A or simply note them with the Ctrl key and click the mouse.
Select the function of creating a panorama.

Panoramas are different and accordingly their projections too. Panoramas are a separate topic, we will talk about them in the article about the panoramas, and now we simply choose the type of Perspective panorama. I filmed on Tilt Shift and I have all the lines of smooth.
Adobe Camera Raw. Slightly thinks and makes you another picture under the already existing three in the list - this will be the stitched panorama.

Now you can work with it as with a regular image, change: exposure, contrast, remove noises, etc. All actions will now be applied to a large panoramic picture in the DNG format (the program itself will offer you to save it as a DNG to keep all the possibilities of the "raw" original).

Then Open File. will turn into Open Object. And you can open a snapshot as a smart object in Photoshop. It is convenient for subsequent work on pulling out shadows, the addition of snapshots, etc. Because By clicking on the layer icon with a snapshot you will get again Adobe Camera Raw. And you can change all the manifests of the image.

On the one hand, it is very cool, and on the other, it greatly increases the size of the file and slows down work with a snapshot.

As you can see, we got a panoramic of 81 MPIXs, you can make a poster of 120 x 50 cm with the quality of the glossy magazine.

RESULTS
Skillful work S. Raw. The converter often eliminates the work in the photoshop itself, so you strongly save time when you use functions Raw. Converter to a greater extent. Plus work in Raw. The converter is not destructive in its essence, i.e. Always something can be canceled or correct.
I hope my impulse of the three parts for writing this article will be useful for you, make your work more efficient. If you want to further see such articles, do not forget to press the repost to social networks (the buttons of VKontakte, Facebook and others are slightly lower in the form of small icons).
Select a parameter to specify where the settings are stored. The use of XMP files is useful if you need to move or save the image file and desire to save the settings of the raw shot. The "Export Settings" command can be used to copy settings from the Camera RAW database to the XMP accompanying files or the settings in the Digital Negative files (DNG).
After processing the image file of a raw shot using Camera RAW, the image settings are saved either in the Camera RAW database file or in the XMP accompanying file. Settings related to DNG files are usually saved directly in DNG files, similar to the TIFF and JPEG file settings.
Note. When importing the sequence of unprocessed snapshot files to the After Effects program, the settings relating to the first file apply to all other files in the sequence that do not have their own accompanying XMP files. The After Effects program does not check the Camera RAW database.
You can specify a parameter to determine the storage location. When you re-open the image file of the unprocessed image, all default settings take the values \u200b\u200bthat were used with the last opening of this file. Image attributes (target color space profile, bit depth, pixel size and permission) are not stored with the settings.
1 In the Adobe Bridge application, select the menu item "Editing"\u003e "Settings Camera Raw" (Windows) or "Bridge"\u003e "Camera Raw" Settings (Mac OS). Or in the "Camera RAW" dialog box, click on the "Open Settings dialog box".
2 In the Camera RAW Setup dialog box, select one of the following "Save Image Parameters" menu options.
Camera Raw Database Saves parameters in the Camera RAW database file located in the Documents and Settings folder / [Username] / Application Data / Adobe / Camerarala (Windows) or Users / [Username] / Library / Preferences (Mac OS). This database is indexed on the contents of the file, which allows you to store the image settings of the raw snapshot even if you move or rename the file of this image.
Accompanying files.xmp Allows you to save the settings in a separate file, in the same folder where the untreated image file is stored, with the same basic name and extension .xmp. This option to save settings can be used to long-term archiving of raw files with related parameters, as well as to exchange raw snapshot files with related parameters in multiplayer workflows. In the same accompanying XMP files, IPTC data (International Press Telecommunications Council) or other metadata belonging to the image file of the raw shot can be stored. Before opening files that are on a CD or DVD media, allowing only reading, be sure to copy them to the hard disk. The Camera RAW external module will not be able to record the XMP file to the media that allows only reading, and instead will record settings to the Camera RAW database file. It is possible to view XMP files in the Adobe Bridge application; To do this, select the "View"\u003e "Show Hidden Files" menu.
Important information. If the file management system is used to manage the files, and the settings are saved in XMP accompanying files, it should be borne in mind that to make changes to images of raw images, it is necessary to carry out the input and output control of the accompanying files; Similarly, control of XMP accompanying files should be ensured (for example, renaming, moving, deleting), along with the corresponding files of raw snapshots. Such file synchronization provides Adobe Bridge, Photoshop, After Effects and Camera RAW applications, if working with files is locally.
If the settings of the raw snapsters are stored in the Camera RAW database, but it is decided to move the files to another location (write on CD or DVD, transfer to another computer, etc.), you can use the "Export Settings in XMP" command to export settings to XMP accompanying files.
3 If there is a need to save all the adjustments made to the DNG files, directly in the files themselves, select "ignore the accompanying files. XMP" in the section "Processing the DNG file" Dialog box "Camera Raw".
Before you directly plunge into a fascinating world of processing, let's get acquainted with the interface and tools of Camera Raw in order to become clear for what to get enough for what "levers" to pull.
It does not matter how the methods described in this you open the file will be met by the interface of the module of this type:
In the center of the "Composition", we are encountered by the Falam Preview Display Window Displays Using Tools, the upper left angle (1), and commands on the menu tabs (6).
Camera RAW file settings
Before processing, you need to configure the parameters for the output ACR file in the "normal" state, they must match the PhotoShop settings. This concerns the choice of color space. I work in SRGB the corresponding color space is selected with me and in ACR, otherwise, when you open the file in Photoshop, the program will offer to convert the file.
From here Moral - why in Camera Raw to suffer with editing, for example, in the Adobe RGB space to immediately lose all the color nuances when you open the file in Photoshop due to the difference in the color coverage between Adobe RGB and SRGB?
- color space;
- color depth;
- the size;
- resolution.
You click on it the "Workflow options" settings dialog where you can change these parameters.

By selecting the appropriate settings, you can enhance the sharpness of "Output Sharpening" Photo for printing or screen, but if further processing is planned to touch these parameters are not worth it, smoothly, as well as the image opening flag in Photoshop as a smart object can do this in another way about it below.
Opening and saving a file in Camera Raw
- Open Image - Opens the file to edit in Photoshop, and if you hold the shift and click on this button, the file will be open as a smart object within which the RAW is processed. This allows during processing to return to ACR to fix the changes made earlier or add new ones, naturally it increases the file size. If the work goes with the group, files selected in this group will open;
- the Cancel button closes the photo without saving changes;
- Dane saves changes and closes the picture.
A mansion is the Save Image button (10) behind which the whole dialog is hidden, allowing you to specify the format and additional parameters for the saved processed file. If you do not plan to further process the file, this button is what you need.

Viewing view
Radom with the save and opening buttons are the buttons (8), allowing you to change the viewing mode edited by the photo in the preview window of the document.

- switching different types of submission "before after", two types of preview of the file are created (controlled by the Q key);
- also switching "before after" but between the settings made (key P). If the work goes with a group of files, how to open multiple images to edit it is written, to switch, you need to press the SHIFT key (SHIFT + P);
- button that allows you to copy the current settings to the "Up" view (combination Alt + P). For a group of files (SHIFT + ALT + P);
- switching between current settings and source status of the picture, default settings (Ctrl + Alt + P).
Conditionally to this group, you can attribute a viewing mode switch, regulating dimensions window module (3) controlled by the F. key
Camera Raw tools
In the upper left corner of the module "cozy" is located block toolsCamera.Raw. Their use plays an important, but not a decisive role in editing the photo. The main load in this case falls on the menu block (6), in which the editing commands of various parameters are collected on the switching tabs of which requires individual publications.
Let's go back to acquaintance with instruments, some of them have analogues in Photoshop others provide specific services:

- the "scale" (ZOOM, Z key) is not needed, about the purpose of which you can guess only by looking at the icon. Scale change can be adjusted using the Save Image button located above.;
- "Hand" (Hard, H) moves an enlarged image inside the preview window;
- White Balance, I) Conveniently use if a gray card is installed in the frame or you clearly imagine which object in the image is medium-gray from it you can take a sample of color and voila. In most cases, "voila" does not occur;
- "Color sample selection" (Color Sampler, S) sets sample markers to 9, for subsequent correction;
- "Target Correction" (Target Adjustments, T). Corrects the picture by dragging the cursor of the mouse over the image;
- "Frame" (CROP, C) The crop tool, however, in contrast to the "fellow" in Photoshop described in the other. Presses only the preview of the preview, to the same RAW file applies only at the time of opening it in Photoshop;
- "Alignment" (Straighten, a) The name speaks for itself;
- "Removing points" (Spot Removal, b) is perfect for removing small defects, the quick retouching has its own settings parameters;
- removal of the effect of red eyes (Red Eye Removal, E) Analog Photoshop is described
- tools used for local corrections, changes made to images, brush (k), graded (G) and radial (J) gradients;
- button opening dialogue module settings (ACR PRESENCES, CTRL + K);
- image rotation tools counterclockwise (Rotate CounterClockWise, L) and on it (Rotate Clockwise, R).
For the tools follow (2) information about the photo received from the camera. Histogram (4) showing photo probe distributions during correction. Information about the parameters of the chamber (5).
Camera RAW interface with file processing
Ate for processing Open group files ACR interface will slightly change

"Filmstrip) (1a) will appear on which the miniatures of open files will be located. To display the desired file in the preview window, it is enough to click on its miniature. The film is equipped with a drop-down menu, equipped with commands:

- Select all files on the tape (Ctrl + A)
- Choice by rating (Ctrl + Alt + A) allows you to select images for which rating is assigned. Assigned estimates allow you to select the most interesting images for processing in the first place.
- Synchronization of settings (ALT + S) between the file open in the viewer window and the group-selected on the ribbon (group processing)
- Creating an HDR image, you need to open specially intended for this files, (Alt + M);
- Creating a panoramic picture (Ctrl + M).
An additional button (2a) appears to delete the selected files. To navigate the film between thumbnails, with the simultaneous opening of the file in the preview window, you can use the buttons (3a), this function has the arrow buttons on the keyboard.
So in a nutshell, the Camera RAW interface in further articles will cut the features and ACR capabilities in detail.
RAW from English is translated as "raw, unfinished." If this quality cannot be considered in the usual life as a plus, then in the digital photography "crude" format is the most perfect. Only the most serious digital cameras allow you to save pictures in RAW to postpone part of important settings before the processing stage and squeeze the maximum of photographic equipment.
What is Raw.
If the universal JPEG and TIFF image formats can be considered a digital equivalent of a slide (or finite print), then Raw is an analogue of the film negative. "Semi-finished product" involving various options for further processing, during which one or another result will be obtained.
To understand the meaning of the "raw" format, it is worth going from the opposite. When using JPEG, the picture passes five steps: capture an analog signal with a matrix, a digital form translating (analog-to-digital converter), color interpolation, processing in accordance with the camera settings, compression with quality loss. Half settings are found in any cameras, including film (exposure, ISO sensitivity, measurement method, autofocus work). The remaining settings are related to the JPEG format: * color rendition. Various options ("live", "saturated", "natural colors"). Monochrome shooting modes. Correction of color components RGB. * White balance. If the snapshot turns out to be blue or red, the incorrect installation of White Ballance is selected. * Brightness and saturation. * Microcontrast. It appears under the English word Sharpening or Russian "sharpness", although there is no relation to the present sharpness. * Compression ratio. Different options like "Super-Fine" in fact, meaning that losses are minimized.
The digital "negative" is recorded on the card immediately after the digitization stage of the analog signal. Its use allows you to postpone all these settings to a PC processing step.
Color interpolation
A typical digital camera matrix consists of cells located on one plane that react only to brightness, forming a monochrome image. To get information about the color, Kodak Engineer Bruce Bayer 20 years ago offered to establish in front of each cell a filter of one of three colors - green, red and blue, which in the amount give the desired shade. This technology is used to this day. Each cell with red and blue filters accounts for two with green, since this color contains basic brightness information.
After converting a digital form, the picture consists of pixels of red, green and blue. For direct work, such an intermediate image is unsuitable. In order for each pixel at the exit to have a natural hue (that is, included all three color components), the camera processor or the RAW converter summarizes the color of the adjacent pixels, for which the complex color interpolation algorithm is used.

Depending on the manufacturer and the specific model of the CFC, the RAW file may contain data both to interpolation and after (before the final processing phase). Most of the modern digital cameras use the first approach, since RAW conversion programs almost always offer more advanced algorithms. In addition, they are constantly being improved, and the camera processor can be changed by buying a new one. Improving intra-ferrous JPEG algorithms is developing in parallel with the improvement of matrices. It is precisely that it often determines the advantages of new models in front of the predecessors - for example, the Nikon D40 mirrors over the D70.
The same matrix, but D40 is a more "fresh" model, and therefore it provides better quality JPEG. But even better quality can be achieved by shooting at D70, if you even refuse JPEG format!
"Raw" quality
The RAW file potentially always more information than in the final one. RAW converters use these data in different ways. Some are better suited for processing under-off-planned pictures, the other "squeeze" the maximum of the removed with the optimal settings.
As a rule, the ADC (analog-to-digital converter) provides a color depth of 12 bits. There are more advanced exceptions: Canon 40D (14 Bit), Fuji S5 Pro (14 Bit X 2), Pentax K10D (22 Bit). When shooting in JPEG format, we get ordinary 8-bit files immediately suitable for printing. "Excess" information is used by the processor to compensate for the disadvantages of the matrix (narrow band of brightness, noise). But even in the most powerful and advanced models, "extra" information is not used 100%. RAW stores all the information that the ADC block gives, including the initial discharge (color depth).


After the files are copied to the computer, you yourself decide what to do with 12-bit data. A 12-bit RAW makes it possible to safely exposure within two exposure steps in each direction. Using the Exposure Tool in the RAW converter (simply moving the slider), you displays the work area of \u200b\u200bthe destination file (8-bit). If your camera is slightly mistaken in the choice of exposure parameters, it will allow you to "pull out" shadows and light without any tonal distortion or other side effects that take place in the event of a serious tone correction.
If the exposure is initially defined exactly, due to greater bit, you can get deeper, detailed images, converting "raw" files into TIFF format with a 16-bit color. The RAW bit allows you to use this format for receiving photos with an extended dynamic range - High Dynamic Range (HDR).
Mature format
If the RAW format coincided with all manufacturers, it would be very convenient from the point of view of software compatibility. In the history there were attempts to create a universal standard of digital negative, similar to JPEG and TIFF. The most successful of them is the Digital Negative format (DNG) from Adobe, which has been used in some modern Central DSC (Leica M8, Pentax K10D, SAMSUNG GX-10). However, this is an exception to the general rule.


Not only that each manufacturer promotes its own standard of "raw" files (CR2, NEF, PEF, variations with the RAW extension), so also inside the line of one manufacturer do not match the formats: as a rule, for each new generation, the CFC requires a software update.
Formats differ not only from the point of view of the data structure. Sometimes manufacturers save space on memory cards using "raw" data compression (for example, as in the case of Nikon Electronic Format). Theoretically, such compression may result in a minor loss of quality. In practice, even minimal losses are absent. The disadvantage is only that the compression process itself takes resources and can affect the recording speed of the pictures. "Raw" Pentax (PEF) format embodies the opposite approach.
When not to shoot in RAW
The RAW format provides better quality and the ability to do even from not the most successful snapshots something that is pleasing. But there are several situations when shooting in RAW is inappropriate: insufficient memory card volume, serial shooting (on some "slow" cameras), household surveys, direct printing, no personal time on image processing.



































