The motherboard is the main connecting link within the computer system unit.
That is why it is very important when purchasing to be able to select from a large assortment of motherboards exactly the one that suits your tasks and satisfies all your requirements. In this article, we will generally look at the main points that you should pay attention to when choosing a motherboard.
For convenience and quick transition, a brief summary is provided:
Motherboard and its main components
In order to better navigate the main components and further visualize for ourselves what we will choose, I suggest that you familiarize yourself with the layout of the motherboard elements using a specific example. For our sample, we took a very original Sapphire Pure Z77K motherboard (original, because Sapphire), which is also aimed at the overclocking market. In fact, for the task of visually examining the main elements of the motherboard, neither the model nor the positioning matters at all. Therefore, let's move on to considering this motherboard:
Click on the picture to enlarge
Here the main components are highlighted with numbers, but some rather specific elements inherent only to overclocking motherboards are also touched upon.
(1) CPU socket- one of the main elements of the motherboard. The processor is installed in the socket and it is very important that CPU socket which it was targeting was compatible with the socket on the motherboard.
Under the number (0) "double" was specified radiator, which is responsible for cooling the elements of the processor power converters, the integrated graphics core and the VTT CPU. Such heatsinks are often found only in motherboards for overclocking. Regular motherboards come without this cooling element.
(2) PCI-Express slots . On the printed circuit board of this motherboard we see 3 PCI-Express X16 version 3.0 slots; these connectors are designed for installing video cards (either one or several in SLI and Cross Fire modes). This also includes the number (3) - it's the same PCI-Express x16 slot, but already an older version 2.0. Between PCI-E X16 slots, numbered (14) posted PCI-E X1 slots. These expansion connectors are designed for installing devices that do not require large bus bandwidth; One X1 line is enough for them. Such devices include TV tuners, audio and network cards, various controllers and many others.
Under the number (4) we have indicated chipset(in this case Intel Z77), which is hidden under the radiator that cools it. The system logic set contains various controllers and is the connecting link between the control of some components and the processor.
(5) Connectors for installation DDR3 RAM. These connectors are painted black and blue for installing memory modules in dual-channel operating mode, which allows them to slightly increase their operating efficiency.
(6) CMOS memory battery. This battery powers the microcircuit CMOS BIOS memory so that it does not lose its settings after turning off the computer.
(8) , (12) 24-pin and 8-pin connectors respectively. 24-pin is the main 24-pin power connector through which most components of the motherboard are powered.
Under the number (9) And (10) connectors are indicated SATA 3 (6 Gb/s) and SATA 2 respectively. They are located on the edge of the motherboard and are made in the style of motherboard connectors for overclocking (connecting devices on the side for open stands). SATA interface used to connect hard drives, SSD drives and drives. In conventional motherboards, they are deployed frontally and shifted closer to the center, which allows them to be conveniently used within the system unit of “non-overclocking” systems.
Under the number (11) a rather specific element was designated, which is found only in motherboards for enthusiasts - this POST code indicator. It also displays the processor temperature, but likes to lie a little.
(13)
Back panel motherboard with external connectors. A variety of peripheral devices such as a mouse, keyboard, speakers, headphones, and many others are connected to the connectors on this panel.
Now that we have gone through the layout of the components on the motherboard, we can move on to considering the individual blocks and parameters for choosing a motherboard. Since this article is introductory, everything will be described briefly and discussed much more deeply in separate articles. So, let's go.
Choosing a motherboard manufacturer
The motherboard manufacturer is not a very important factor when choosing. The situation here is absolutely identical as with manufacturer's choice for video card- everyone is good and the question here is rather “religious” - who believes in what. Therefore, you can safely choose from all the “no name” manufacturers such as Asus, Biostar, ASRock, Gigabyte, Intel and MSI. Even the motherboard from the unknown in the motherboard market, Sapphire, which we took to review the main components, is a good example. Perhaps some boards have a not very convenient layout, perhaps some manufacturer’s package is not very extensive, and some may have a box that is not as bright as we would like - but still, all this does not give us the right to single out someone. then one, as an impeccable leader and answer the question: which motherboard is better within the framework of the manufacturer’s assessment.
![]()
All motherboards will eventually come with the same chipsets from AMD and Intel, and will be functionally similar. The only thing is that before purchasing, I advise you to review reviews of motherboards and user reviews, so as not to run into a model with unsuccessful cooling or something else. We will not dwell on the choice of motherboard manufacturers for long, but rather move on.
Choosing the right form factor
Initially, the correct choice of form factor will save you from many problems in the future. At the moment, the most popular form factors of motherboards are ATX and its stripped-down version – Micro-ATX.
The fact that the form factor determines the further expandability of the system is very important. The Micro-ATX form factor usually has fewer PCI and PCI-E expansion slots for video cards and additional devices. Also, often, such motherboards have only two slots for installing memory modules, which significantly limits the expansion of RAM, both quantitatively and in terms of convenience issues. But the main advantage of Micro-ATX lies in the price. Based on the description of these two standards, it can be argued that Micro-ATX is positioned as a budget solution for compact office and home systems.
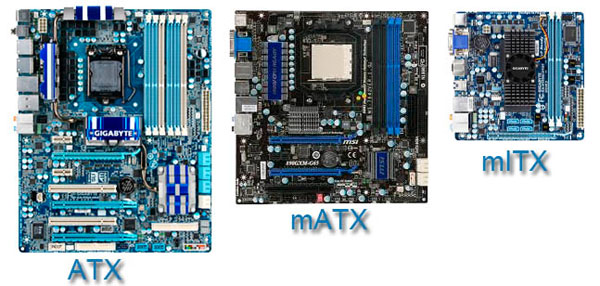
The size is also important, as it follows from the form factor. ATX boards are much larger than their “Micro” brothers, so you should take into account the size of the case in relation to the size of the motherboard.
The form factors and their features will be described in more detail in a separate article.
Choosing a motherboard socket
Once you have decided on the processor, the selection of the motherboard begins. And the first factor of choice should be the socket, which ensures compatibility between the processor and motherboard. That is, if an Intel processor with an LGA 1155 socket was selected, then the motherboard must also have an LGA 1155 socket. A list of supported sockets and processors can be found on the motherboard manufacturer’s website.
You can find out more about modern processor sockets in the article: CPU socket.
Choosing a motherboard chipset
The chipset is the connecting link between the entire system. It is the chipset that largely determines the capabilities of the motherboard. Chipset- this is initially a “set of chips” of system logic, which consists of a north and south bridge, but now this is not so simple.
Today, the latest 7-series chipsets from Intel and the 900-series from AMD are popular, and Nvidia is also joining them, but the range of chipsets there is quite small.
Chipsets of the seventh series of Intel such as Z77, H77, B75 and others have slightly distorted the concept of “chipset”, because they do not consist of several chips, but only of a north bridge. This in no way reduces the functionality of the motherboard, because some of the controllers were simply transferred to the processor. Such controllers include a PCI-Express 3.0 bus controller and a DDR3 memory controller. The North Bridge was given control of USB, SATA, PCI-Express, etc. What is connected to what and on what buses is clearly visible in the block diagram of the Z77 chipset:
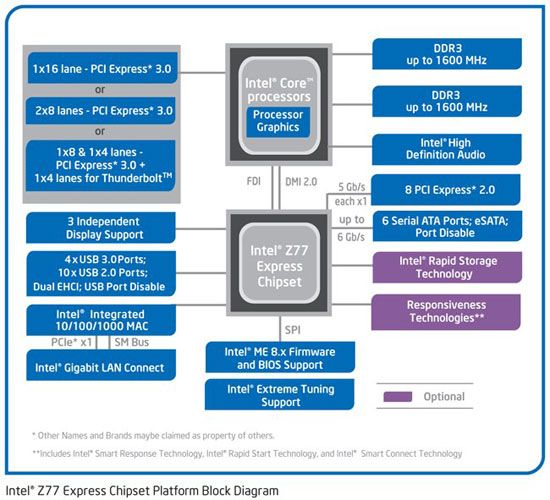
Indices Z, H, B - mean the positioning of a particular chipset for different market segments. Z77 was classified as a chipset for overclocking enthusiasts. H77 is a regular mainstream chipset with advanced functionality. B75 is a slightly trimmed H77 in terms of capabilities, but for budget and office systems. There are other letter indices, but we will not dwell on them in detail.
Chipsets from AMD continue the tradition of dual-chip chipsets and the latest 900 series is no exception. Motherboards with this set of system logic are equipped with 990FX, 990X 970 north bridges, as well as SB950 south bridge.
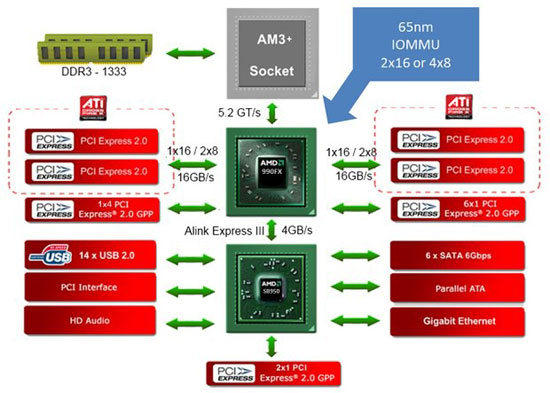
When choosing a northbridge for an AMD motherboard, you should also take into account its capabilities.
The 990FX is a northbridge designed for the enthusiast market. The main feature of the chipset with this northbridge is its support for 42 PCI-Express lanes. Therefore, on the 32 lines allocated for video adapters, you can connect up to 4 video cards in a Cross Fire combination. From this we conclude that only a few users need such capabilities, so the functionality of motherboards with this chipset will be redundant for most users.
990X and 970 are versions with slightly reduced capabilities. The main difference, again, is in the PCI-Express lines. Both of these north bridges support 26 lines, but this is unlikely to be a problem for anyone. It is worth noting that the 970 does not have support for SLI and Cross Fire, as a result of which it will not be of interest to users who plan to combine more than one video card in the system, but due to its reasonable price, the 970 will look very tasty for a wide audience of users limited to one video card.
The capabilities of AMD and Intel chipsets will be discussed in more detail in a separate article.
Memory slots and PCI-Express
The number of connectors for installing memory and PCI-Express expansion slots is an important factor when choosing a motherboard. As we said above, the number of these same connectors is often determined by the form factor. Therefore, if you are counting on seriously and conveniently scaling the amount of RAM, then it is better to take a closer look at motherboards with 4 and 6 slots for installing RAM. This also applies to PCI-Express slots: it’s stupid to take a Micro-ATX motherboard if you expect to install three video cards in SLI or Cross Fire.
Also, it is very important to pay attention to the type of RAM that the motherboard supports. Nowadays you can still find motherboards with supported DDR2 memory types on sale. When assembling a new system from scratch, it is better not to go back to the past and take a motherboard with DDR3 memory type.
The version of the PCI-Express bus is not an important factor, so you shouldn't be too keen on PCI-Express 3.0 support. For modern video cards, version 2.0 is sufficient. Yes and backwards compatible No one has canceled the various versions of this interface.
External connectors
The presence of certain connectors on the rear panel of the motherboard is quite important. Their number is also important. If we take into account the USB ports, then there should be, let’s say, quite a few of them, since, in most cases, a mouse, keyboard, webcam, printer, scanner and a large variety of other devices are connected there.

You should pay attention to the audio connectors of the integrated sound card: there can be either three or six. Three connectors are enough for a standard circuit: microphone, headphones and subwoofer. If you plan to use multi-channel acoustics, then you need to look towards motherboards with 6 connectors. But even if you are not currently planning to purchase such acoustics, the connectors will not hurt, and they may be very useful in the future. And for office and budget systems, 3 audio connectors are more than enough.
In addition, two LAN connectors may be useful; for this, two network controllers must be soldered on the board. But for most users, one network connector will be enough.
Additional features
Additional features include functionality that is not in demand for the average user, but for some can be very useful:
- ESATA is an interface for connecting removable drives; it is not present in all motherboards and can be a very useful feature for owners of external drives.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth module - integrated wireless network and data transfer modules can significantly improve the functionality of the motherboard.
- Thunderbolt is a new interface for connecting peripheral devices and provides data transfer at speeds of up to 10 Gb/s, which is 20 times faster than the now popular USB 2.0, and 2 times faster than USB 3.0.
A very specific interface that only a few people will need today, but which promises to gain great popularity in the future.

- This also includes special buttons and indicators on motherboards for overclocking. It can also be various branded elements and technologies from the manufacturer.
conclusions
Choosing a motherboard is not such an easy task. It is necessary, based on all the parameters, to select an option that will be satisfactory both in functional terms and in terms of cost. You need to be able to catch that fine line of the price/performance ratio. It should be remembered that everything is very individual and the best motherboard for your friend may be the worst option for your needs.
But if you focus on the basic parameters and approach the issue comprehensively, then the choice will be correct and will fully satisfy all your expectations.
P.S. We will try to answer your questions like “which motherboard should I buy?”, “which motherboard is better?” etc., in the comments to the article or on our forum.
Thank you for your attention. Good luck with your choice!