Hello everybody! Sometimes there is a need to replace the processor in your computer. The reason for this may be a breakdown or upgrade. And in this article I will tell you how to choose a processor.
Let's figure out first how to choose a processor. The processor is selected according to the following features:
- Manufacturer
- Cash processor
- Availability of built-in video
Now consider each parameter separately.
1. Let's start with the manufacturer. There are only two processor manufacturers: Intel and AMD. No one can say which one is better, because both firms are good. Which processor choose is an individual, I can only say that AMD processors are cheaper. Choose depending on the configuration of your computer. If for a powerful gaming computer - it is better to take Intel. For others will go and AMD. Read more I wrote an article.

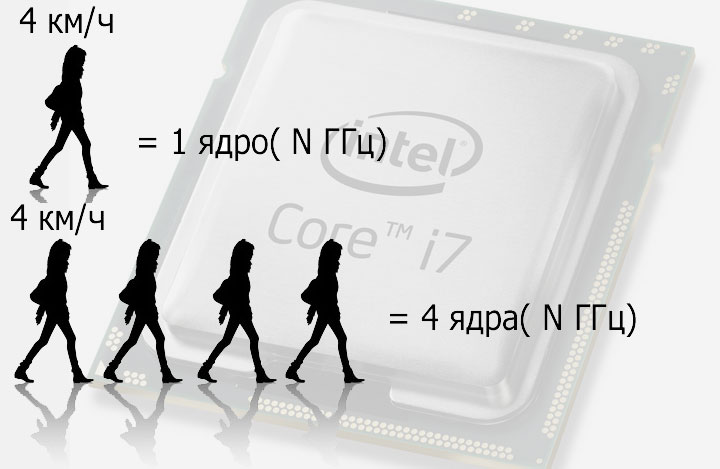
2. Next, the number of nuclei. If you have a computer for games, you need a minimum of 4 kernels. For the computers of the middle configuration, dual-core (because mostly programs are used only 2 and even if you have 4 of them, then the program will still use 2). There are no less than the kernels in any processor (from new, not counting the old processors used).
I will explain as clearly as possible: the more frequency, the faster the processor will form. That is, the more frequency, the more it can perform operations in one second. Try to search for a processor with a minimum frequency of 2.6-2.7 GHz.
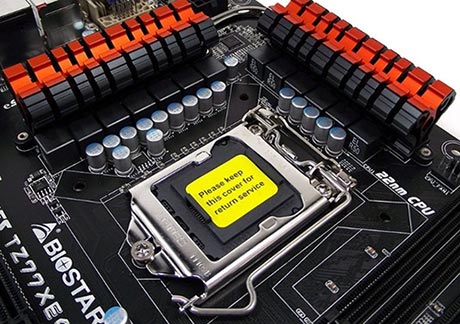
In my opinion it is the most important point. Newbies especially need to know, otherwise 100% will buy not the processor that is needed. In general, the socket is. Their different, all sorts of many: Intel - Socket 1150, Socket 1155; AMD - Socket AM3, AM3 +, FM2. This is not all, these are just examples. The name of the processor socket must coincide with the name of the socket on the motherboard. Otherwise, you just can't insert the processor into the socket.
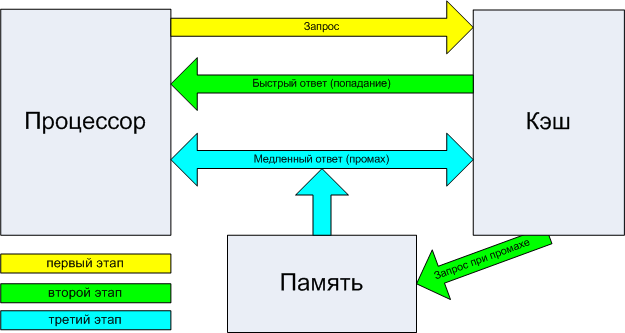
5. Cash processor. Shows one of the main parameter when choosing! There is cache 1, 2 and 3rd levels. It is so to speak the processor's operational memory than it is more, the amount of greater information will be processed faster. 1y the fastest and smallest, and the 3rd is the slowest and large. Sometimes there are only 2 levels on weaker processors. Outcome: the more cache, the better.
The more heat dissipation, the more effective will have. Accordingly, the less, the better.

Technologies that increase performance. For example, SSE 2,3,4, 3DNow, NX BIT and many others ... I especially pleased with the Intel VPRO technology, thanks to which, you can ask for Intel technical support to block your laptop if it was suddenly stolen.
I will not fool your head with all sorts of semiconductors, as everywhere is described ... You can read the scientific description in Wikipedia. In a simple embodiment, the smaller the technical process, the fewer the parts in the processor are used, and therefore, with minimal sizes, it can be achieved greater power. The less size the better, in my i7 technical process 22 nm ... Intel threatens by 2018 to introduce 10 nm ...
9. And the latter is the presence of a built-in graphics core. I will be brief and I will explain as simple as possible. When the processor has a built-in graphic core - it means that there is a built-in video card. Built-in video cards are on many motherboard, but they will only work with the embedded graphics core in the processor. But not all embedded video cards need this core. In principle, this item is not very important, but it will not be superfluous.

That's all! The main thing is to choose the last socket, a big cache, and the rest of your needs and you can choose an excellent processor! Good luck!