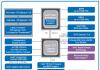
Which provides the operation of all computer items. The chipset also determines the performance and power of the computer.
Physically, the chipset is one or more large chips on the motherboard and several auxiliary microcircuits, smaller sizes. These chips during the work are heated, so the manufacturers of motherboards are installed on them radiators for cooling.
By virtue of the established engineering traditions, the main chipset chips were called: North Bridge and South Bridge.
The main function of the northern bridge:
Communication processor with memory, video card and southern bridge.
The main function of the southern bridge:
Provides communication with processor, with all other devices (hard drives, extension cards, USB devices, etc.).
Currently, there are processors that themselves can perform the functions of the Northern Bridge. Therefore, in motherboards for such processors, there is no north bridge, there is only southern!
Basic chipset manufacturers:
- Intel
- NVIDIA
Basic manufacturers of chipset for desktop PCs - Intel and AMD. Some time ago, NVIDIA chipsets also produced.
Definitely say that some kind of direction is better - it is impossible. In both firms there are products, on the basis of which you can collect an office and powerful gaming computer.
Therefore, when choosing an architecture, that is, Intel or AMD, a big role is played - the personal preference of the buyer or the seller.
Characteristics of the chipset that affect computer performance
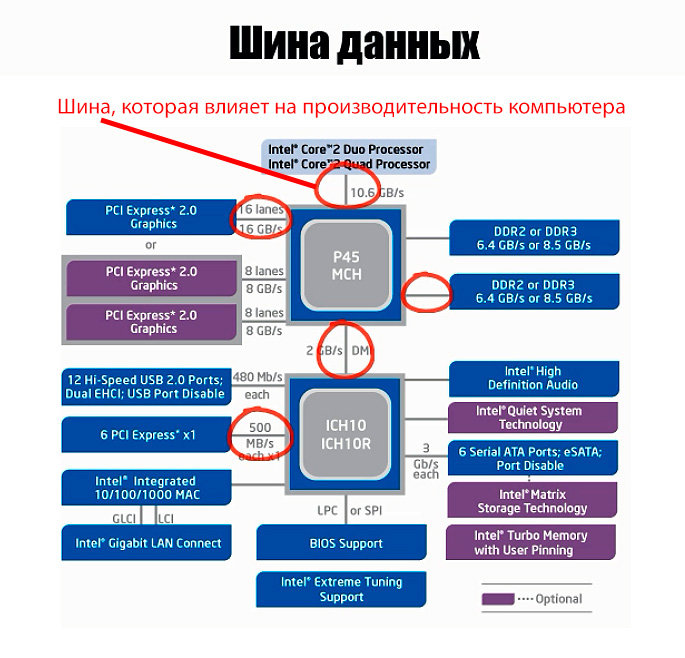
Data bus - This is a tire, designed to transfer data between PC nodes.
All components of the computer interact with the chipset through the data bus. Each tire works with its speed, but it affects the performance of the computer, the tire that connects the chipset and processor. This parameter of the data bus is indicated as a bus frequency or tire bandwidth.
The data bus has two characteristics, frequency and width.
Frequency - This is the actual speed of the tire. Usually measured in megahertz or gigahertz. The higher the frequency, the higher the performance of the system.
For example: 1333 MHz, 1600 MHz
Width - This is the number of bytes that the tire can transmit at once or per rat. The larger the width, the more information can transfer the tire for one beat.
For example: 1 byte, 2 bytes.
Data bus bandwidth
The product of frequency on the width gives another parameter - data bus bandwidth.
Frequency * Width \u003d Data bus bandwidth - the amount of information that can transmit bus per second.
Example # 1: Frequency 4 GHz and width 1 byte - we obtain bandwidth, 4 * 1 \u003d 4 GB per second (4GB / s or GB / S).
Example # 2: Frequency 2 GHz and width 2 bytes - We obtain bandwidth, 2 * 2 \u003d 4 GB per second (4GB / s or GB / S).
That is, with a lower frequency, but greater width - we will get the same bandwidth of the data bus. For the processor, these two options in performance are equivalent.
Due to the fact that in new chips implemented a new data bus architecture. A new parameter was introduced - transfers per second.
Transfers per second
Transfers per second - This is the number of data transfer operations per second.
This parameter also refers to bandwidth but already means not the volume, but the number of operations that the tire can transmit per second.
Typically, the number of transfers per second, twice the frequency of the data bus.
For example: 5200 mt / s, 5200 mt / s (Megatransfer per second)
5.2 GT / C, 5.2 GT / S (Gigatransfer per second)
In the description of the motherboard, the maximum possible speed of the data bus, which connects the processor and the chipset is indicated. In fact, the speed of the tire will depend on the installed processor. This is due to the fact that the processor has the same characteristic as the frequency of the tire or the speed of the tire. If it is lower than that of the chipset, the speed of the data tire will be such as the processor.
As designated chipset in the description of the board
Characteristics of the chipset in a brief description:
ASUS P7H55 -V; S1156; without ffd!; Support Core i3, i5, i7; HH5; 4DDR3 (2200 *); 1xp-ex16, 3xp-ex1; 3XP; 8ch-Sound; Gigalan; 6XSATAII; 1xata100; ATX
Usually, the chipset is already specified in the name of the motherboard: ASUS P7H55 -V and then it is specified in a brief description after, and in more detail in full description of the board.
Characteristics of the chipset in the detailed description:
- System Tire Frequency
- Tire frequency
- Data genus frequency
- System Bus.
- Front Side Bus, QPI, Hyper Transport