GSM900, DCS1800, UMTS2100, CDMA450, 3G, 4G LTE.
Uplink. - Channel of communication from the subscriber (phone or modem) to the base station of the cellular operator.
DOWNLINK. - Channel of communication from the base station to the subscriber.
GSM frequency
GSM is the link of the 2nd generation. GSM 900 frequency range: uplink 890-915 MHz, DOWNLINK 935-960 MHz. There is an optional GSM frequency range, the so-called E-GSM is an additional 10 MHz. E-GSM: UPLINK 880-890 MHz, DOWNLINK 925-935 MHz.
Frequency 3G.
3G Total 3rd Generation Communication. In Russia, it works at frequencies: uplink 1920 - 1980 MHz and DownLink 2110 - 2170 MHz. Also, the Skylink operator has a frequency of 3G in the CDMA 450 standard standard: uplink 453-457.5 MHz and DOWNLINK 463-467.5 MHz.
Frequency 4G LTE
4G cellular 4th generation. In Russia, it works in 4G LTE (Long-Term Evolution) at frequencies: 2500-2700 MHz.
CDMA frequency
The CDMA 450 works Skylink and W-CDMA (UMTS) operators "Big Troy" operate. Skylink CDMA Frequency - uplink 453-457.5 MHz and DownLink 463-467.5 MHz. W-CDMA (UMTS) - UPLINK 1920 - 1980 MHz and DownLink 2110 - 2170 MHz.
Frequencies Umts.
UMTS (Eng. Universal Mobile Telecommunications System - Universal Mobile Telecommunication System). Actually, this is 3G. UMTS Frequency: UPLINK 1920 - 1980 MHz and DownLink 2110 - 2170 MHz.
Frequency amplifiers (repeater) cellular communication.
If you need only voice communicationThe GSM repeaters are suitable with 900 MHz frequencies or DCS 1800 MHz (Vector, AnyTone). If you need the Internet, the frequency of the repeater must coincide with the frequencies of 3G / UMTS 1920-2170 MHz.
Frequencies GSM Russia
GSM 900: UPLINK 890-915 MHz, DownLink 935-960 MHz. A total of 124 channels in GSM900. In each region of Russia, the GSM frequency is distributed between cellular operators individually.
GSM 1800 frequencies.
The GSM 1800 standard is correct to call DCS1800. Its frequencies - uplink 1710-1785 MHz and downlink 1805-1880 MHz.
3G frequency range.
3G - In Russia, this is CDMA450 (Skylink) and UMTS 2100. UMTS frequency range: uplink 1920 - 1980 MHz and DownLink 2110 - 2170 MHz, A CDMA450 - UPLINK 453-457.5 MHz and DOWNLINK 463-467.5 MHz. For example, the Beeline cell operator in the Moscow region tests its 3G in the GSM900 frequency range. 3G frequencies for other regions of Russia are the same: uplink 1920 - 1980 MHz and DOWNLINK 2110 - 2170 MHz
Frequencies 3G modems.
As a rule, all 3G modems operate at 3G / UMTS: UPLINK 1920 - 1980 MHz and DOWNLINK 2110 - 2170 MHz., And maintain frequencies of 2G networks, that is, GSM900: uplink 890-915 MHz, DownLink 935-960 MHz and DCS 1800 (He is GSM1800) Uplink 1710-1785 MHz and DownLink 1805-1880 MHz.
The largest operators Communication of Russia.
Skyline frequency.
The existing network Skylink CDMA450 - Uplink 453-457.5 MHz and DOWNLINK 463-467.5 MHz. In September 2010, Skylink received a frequency license 2100, namely 1920 - 1935 MHz and DownLink 2110 - 2125 MHz.
MTS 3G frequency.
UPLINK 1950 - 1965 MHz and DownLink 2140 - 2155 MHz. MTS like others cellular operators In the 3G range has a width of 15 MHz.
3G / UMTS megaphone frequency.
MegaFon in the 3G / UMTS range operates at frequencies: uplink 1935 - 1950 MHz and DOWNLINK 2125 - 2140 MHz.
Beeline frequency 3G.
Beeline in the Moscow region tests its 3G in the GSM900 frequency range. 3G frequencies for regions of Russia: uplink 1920 - 1980 MHz and DOWNLINK 2110 - 2170 MHz
Frequency Megaphone 4G.
MegaFon in the 4G range operates at frequencies: 2500 - 2700 MHz.
Frequency Yota 4G LTE
the Internet yota. It works in the 4G LTE range at frequencies: 2500 - 2700 MHz.
The beginners are incomprehensible to the games taken by the developers of standards. It would seem, uses GSM frequencies 850, 1900, 900, 1800 MHz, which is more like? Quick response - read the Network Telephone Instruction section. The unlawfulness of the generally accepted interpretation will be shown. The problem is described by the following provisions:
- The second generation of 2G cellular communication has generated a lot of standards. The world knows three epicenter, asking Rhythm: Europe, North America, Japan. Russia adopted the standards of the first two, reinforcing.
- The pedigree tree of standards is constantly carrying.
- International standards options are designed to unite the heterogeneous rules of individual countries. Often it is impossible directly directly. Governments change the legislative base by fixing frequency plans.
This explains the origins of misunderstanding problems with beginners. Returning the subject of clarity, we will build a simplified hierarchy of standards, indicating the frequencies used passable.
Genealogy standards
The following information is designed to clarify the inhabitant the structure of existing, extinct standards. Below, in the following sections, technology used in Russia will be described. The corresponding representatives of the Tree, decorated Russian forest, are fed.
1G.
- AMPS family: AMPS, NAMPS, TACS, ETACS.
- Others: NMT, C-450, Datatac, Hicap, Mobitex.
2G: 1992.
- GSM / 3GPP: GSM, HSCSD, CSD family.
- Family 3GPP2: CDMaOne.
- AMPS family: D-AMPS.
- Other: IDEN, PHS, PDC, CDPD.
2G +.
- Family 3GPP / GSM: GPRS, EDGE.
- Family 3GPP2: CDMA2000 1X, including Advanced.
- Others: Widen, DECT.
3G: 2003.
- Family 3GPP: UMTS.
- Family 3GPP2: CDMA2000 1xEV-Do R. 0
3G +.
- Family 3GPP: LTE, HSPA, HSPA +.
- Family 3GPP2: CDMA2000 1XEV-DO R. A, CDMA2000 1XEV-DO R. B, CDMA2000 1XEV-DO R. C
- IEEE: Mobile WiMAX, Flash ofDM.
4G: 2013.
- Family 3GPP: LTE-A, LTE-S Pro.
- IEEE: WiMAX family.
5G: 2020.
- 5G-Nr.

Short description
Genealogy allows you to trace extinct views. For example, modern authors often use GSM abbreviation, entering a deception reader. The technology is entirely limited by the second generation of cellular communication, extinct view. Former frequencies with additions continue to be used by descendants. On December 1, 2016, the Australian Tellest stopped using GSM, becoming the first operator in the world, entirely updating the equipment. The technology continues to be content with 80% of the world's population (according to GSM Association). An example of the Australian colleagues on January 1, 2017 was followed by American AT & T. The service stops the Optus operator, April 2017 Singapore, acknowledged 2G inconsistency with the increasing needs of the population.
So, the term GSM is used in relation to obsolete equipment, taking the Russian Federation. The descendant protocols can be called GSM heirs. The frequencies are saved by the following generations. Plugs are changing, information transfer methods. The aspects of the frequency distribution, accompanying the modernization of the equipment. Information is required to establish GSM kinship.
Telephone instruction
Useful information regarding the question will provide the phone instruction. The corresponding section lists the supported frequencies. Separate devices will allow you to adjust the reception area. You should choose a model of the phone, catching generally accepted Russian channels:
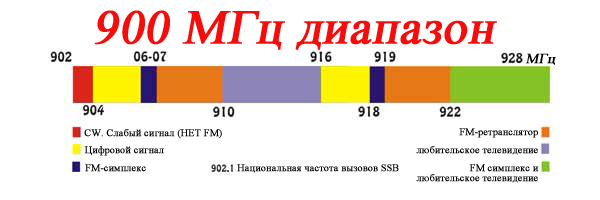
- 900 MHz - E-GSM. Rising branch - 880..915 MHz, descending - 925..960 MHz.
- 1800 MHz - DCS. Rising branch - 1710..1785 MHz, descending - 1805..1880 MHz.
LTE technology adds an area of \u200b\u200b2600 MHz, an 800 MHz canal is introduced.
History of the Communications RF: Frequency
In 1983, the development of the European Digital Standard was launched. We remind you, the first generation of 1G used analog transmission. Thus, engineers developed in advance the standard, proactive the history of the development of technology. Digital communication was born of World War II, more precisely, the cipher system was a green hornet. The military understood perfectly: the era of digital technologies is becoming. Civil industry caught wind movement.
900 MHz
The European CEPT organization has created the GSM Committee (Groupe Special Mobile). The European Commission proposed to use the 900 MHz spectrum. The developers sat down in Paris. Five years later (1987), 13 EU countries filed Copenhagen Memorandum of the need to create a unified cellular network. The community decided to request GSM assistance. In February, the first data sheet. Policies of four countries (May 1987) supported the project by the Bonn Declaration. The next short period (38 weeks) is filled with universal bustle, controlled by four designated persons:
- Armin Zilberhore (Germany).
- Philip Dupulis (France).
- Renzo Faili (Italy).
- Stephen Temple (United Kingdom).
In 1989, the GSM commission leaves the CEPT guardianship, becoming part of ETSI. On July 1, 1991, the former Prime Minister of Finland, Harry Holzer, made the first call to the Subscriber (Kaararin Suonio), using the services of the Radio Provider.
1800 MHz
In parallel, the introduction of 2G was work designed to use the 1800 MHz region. The first network covered the United Kingdom (1993). At the same time, an Australian telecom operator was put on.
1900 MHz
The frequency of 1900 MHz was introduced by the United States (1995). A GSM Association has been created, a global number of subscribers has reached 10 million people. A year later, the figure has increased tenfold. The use of 1900 MHz prevented the introduction of the European version of UMTS.
800 MHz
The 800 MHz range appeared in 2002, in parallel to the implementation of the multimedia messaging service.
Attention, question!
What frequencies have become a Russian standard? Confusion adds ignorance by authors of Runet standards received official developers. The direct response is discussed above (see the Telephone Instruction section), describe the work of the mentioned organizations (UMTS section).
Why so many frequencies
Exploring the results of 2010, the GSM Association said: 80% of the planet's subscribers are covered by the standard. This means that four fifths cannot choose a single frequency. In addition, there are 20% of alien communication standards. Where does the root of evil come from? The countries of the second half of the twentieth century developed fragmented. Frequencies 900 MHz USSR occupied military, civilian air navigation.

GSM: 900 MHz
In parallel to the development of the first variants of GSM NPO Astra, Radio Research Institute, the Research Institute of the Ministry of Defense, the studies ended with the internal tests. Received verdict:
- It is possible to jointly function navigation and second generation of cellular communication.
- NMT-450.
Note: Again 2 Standards. Each uses its own frequency grid. The declared competition of the distribution of GSM-900 won NPO Astra, MGTS OJSC (now MTS), russian companies, Canadian BCeti.
NMT-450MHz - the first generation
So, Moscow used, since 1992, the range of 900 MHz (see above), because other GSM frequencies have not yet been born. In addition to NMT (Nordic cell phones) ... Initially, the Scandinavian Peninsula countries have developed two options:
- NMT-450.
- NMT-900 (1986).
Cause of choice by the Russian government of the first answer? Probably decided to try two ranges. Please note the specified standards describe analogue link (1G). The developers countries began to cover the shop from December 2000. The latter (September 1, 2010) surrendered to Iceland (Siminn). Experts note an important advantage of a range of 450 MHz: range. Weighing plus, appreciated by remote Iceland. The Russian government wanted to cover the country area, using the minimum of the highest.
NMT loved fishermen. The liberated grid took digital CDMA 450. For 2015, Scandinavia technology mastered 4G. Russian Uralvestian released the Camork on September 1, 2006, Sibirtelecom - January 10, 2008. The child's subsidiary (body 2) scores the Perm region, Arkhangelsk region. The deadline for the end of the license is 2021.
D-amps: DMW (400..890 MHz) - second generation
American networks 1G, used AMPS specification, refused to receive GSM. Instead, there are two alternatives to organize mobile networks second generation:
- IS-54 (March 1990, 824-849; 869-894 MHz).
- IS-136. Differs in a large number of channels.

The standard is now dead, universally replaced by the descendants of GSM / GPRS, CDMA2000.
Why do Russian D-amps
The Russian manual often uses used appliances. D-AMPS equipment has reached the warehouses of the body 2, Beeline. November 17, 2007 Latest covered the center of the central region. The license of the Novosibirsk region expired on December 31, 2009. The last swallow flew on October 1, 2012 (Kaliningrad region). Kyrgyzstan used range until March 31, 2015.
CDMA2000 - 2G +
Some protocol variants are used:
- Uzbekistan - 450 MHz.
- Ukraine - 450; 800 MHz.
In the period December 2002 - October 2016 Specifications 1хRTT, EV-DO Rev. A (450 MHz) was used skype. Now the infrastructure is upgraded, LTE is implemented. On September 13, 2016, world portals had the news: Tele 2 stops using CDMA. American MTS began the process of introducing LTE a year earlier.
GPRS - second-third generation
The development of the CellPac protocol (1991-1993) was a turning point of cellular development. Received 22 US patent. The descendants of technology consider LTE, UMTS. Batch data transfer is designed to speed up the information exchange process. The project is intended to improve the GSM network (frequencies are listed above). The user is obliged to obtain technologies:
- Access to the Internet.
- Outdated "Click to talk."
- Messenger.
The overlays of two technologies (SMS, GPRS) explicitly accelerates the process. The specification supports IP, PPP, X.25 protocols. Packages continue to come even during a conversation.
Edge.
The next stage of the Evolution of GSM is conceived by AT & T companies (USA). Compact-edge took a niche d-amps. Frequencies are listed above.

UMTS - Full 3G
The first generation required to update the equipment of base stations. The frequency grid has changed. The limit transmission rate of the line using the advantages of HSPA + is 42 Mbps. Really achievable speeds are significantly overlapped with 9.6 Kbps GSM. Since 2006, countries have started updating. Using orthogonal frequency multiplexing, the 3GPP committee intended to reach 4G. Early birds were released in 2002. Initially, the developer laid the following frequencies:
- .2025 MHz. Rising connected branch.
- .2200 MHz. Downward connected branch.
Since the United States has already used 1900 MHz, then selected segments 1710..1755; 2110..2155 MHz. Many countries followed the example of America. The frequency of 2100 MHz is too often busy. From here, the numbers at first:
- 850/1900 MHz. Moreover, 2 channels are chosen using one range. Either 850 or 1900.
Agree, it is incorrect to ship GSM, following a bad spread example. The second generation used a half-duplex single channel, UMTS - used two (5 MHz width) at once.
UMTS Frequency Grid
The first attempt to distribute the spectra took place on February 3 to March 3, 1992. The decision has adapted the Geneva Conference (1997). It is the S5.388 specification that secured the ranges:
- 1885-2025 MHz.
- 2110-2200 MHz.
The decision demanded further refinements. The Commission identified 32 ultra-channel, 11 amounted to an unused reserve. Most others received clarifying names, since individual frequencies coincided. Russia has rejected European practices, despusting the United States, accepting 2 channels (Band) UMTS-FDD:
- №8. 900 MHz - E-GSM. Rising branch - 880..915 MHz, descending - 925..960 MHz.
- Number 3. 1800 MHz - DCS. Rising branch - 1710..1785 MHz, descending - 1805..1880 MHz.
Characteristics cell phone It should be chosen according to the information provided. Wikipedia Table, revealing frequency plan of the planet Earth, is completely useless. Forgot to take into account the Russian specifics. Europe operates nearby channel №1 IMT. In addition, there is a UMTS-TDD grid. The equipment of two air network options are incompatible.
LTE - 3G +
Evolutionary continuation of the GSM-GPRS-UMTS bundle. May serve as an add-on CDMA2000 networks. Only a multi-frequency phone is able to provide LTE technology. Experts directly indicate the place below the fourth generation. Rotating statements of marketers. Initially, the ITU-R organization recognized the technology of the appropriate, later the position was revised.

LTE are a registered trademark ETSI. Key idea The use of signal processors and the introduction of innovative modulation methods of carrier. The appropriate IP addressing of subscribers was recognized. The interface lost backward compatibility, the frequency spectrum has once changed. The first grid (2004) is launched by the Japanese company NTT Docomo. Moscow The exhibition version of technology will overtake in 2010.
Repeating UMTS experience, the developers have introduced two options for the air Protocol:
- LTE-TDD. Temporary division of channels. Technology is widely supported by China, South Korea, Finland, Switzerland. The presence of the sole frequency canal (1850..3800 MHz). Partially overlaps WiMAX, an upgrade is possible.
- LTE-FDD. Frequency division of channels (separate downward, ascending).
Frequency plans 2 technologies are different, 90% of the kernel design coincides. Samsung, Kluckoms produce phones capable of catching both protocols. Ranges occupied:
- North America. 700, 750, 800, 850, 1900, 1700/2100, 2300, 2500, 2600 MHz.
- South America. 2500 MHz.
- Europe. 700, 800, 900, 1800, 2600 MHz.
- Asia. 800, 1800, 2600 MHz.
- Australia, New Zealand. 1800, 2300 MHz.
Russia
Russian operators have chosen LTE-FDD technology, use frequencies:
- 800 MHz.
- 1800 MHz.
- 2600 MHz.
LTE-A - 4G
Frequencies remained the same (see LTE). Launch chronology:
- On October 9, 2012, Yota appeared 11 base stations.
- MegaFon February 25, 2014 covered the garden ring of the capital.
- Beeline from August 5, 2014 works on frequencies LTE. 800, 2600 MHz.
In stock Kits working in all the ranges of cellular frequency frequencies present on the territory of the Russian Federation. Each kit is selected individually for the needs of the facility by the sales managers on the basis of the data obtained during the preliminary measurements carried out by the plan of the building (Floors, Metraja, the material of the bearing walls and partitions).
This is done with one goal - the client is literally immediately after mounting the repeater kit receives a powerful, stable, not interrupted cellular signal in all rooms, including basements. The equipment can be installed in any building (residential, non-residential type), in a country house or in the country area.
Cellular amplifier kits are selected by our specialists after a detailed agreement with the customer.
Thanks to the finished kits "Daltsvyaz", which includes a complete list of the necessary equipment, the client disappears the need for a dozakupka of the lack of cables or other components. We offer our customers more than fifteen options for repeater sets that are selected individually.
We can offer, both ready-made solutions, and to ensure the equipment exclusively under the requirements of the customer and the specifics of the object, where it is necessary to strengthen the cellular signal and the mobile Internet.
We will select a cellular amplifier kit individually
Our company offers 2G GSM, 3G UMTS, 4G LTE signal signal gains. The range of our production includes equipment that allows you to solve absolutely all problems associated with the coating of the cellular network. Repeators function in various frequency ranges. We can also offer models of amplifiers that work simultaneously immediately in several frequency bands.
For all issues of selection, acquisition, installation and configuration, you can consult with the specialists of the company Daltsvyaz, which is one of the leading manufacturers of signal gain systems. mobile communications In Russian federation.
Extended warranty!
Only in our company there is an extended guarantee (from two to five years) to all equipment and components!
Professional approach in work
We are responsible for the fulfillment of our work, we value our reputation, so we propose a signal gain kits selected under the residential / non-residential object exclusively taking into account the requirements of the facility, the wishes of the client.
The use in Western European countries a number of analog cellular standards, non-compatible with each other and having significant drawbacks in comparison with digital standards, led to the need to develop a single pan-European digital cellular standard GSM-900. It provides high quality and communication confidentiality, allows subscribers a large set of services. Standard allows you to organize automatic roaming. As of July 1999, the share of subscribers gSM standard-900 was: in the world about 43%, in Western Europe more than 85%.
The GSM standard is also known as DCS (Digital Cellular System) or PCN (Personal Communications Network), as well as a modification of the GSM-900 standard for a range of 1800 MHz: GSM-1800 standard. The GSM standard includes the most complete set of services compared to others.
The GSM cellular networks are initially designed as a large capacity network, calculated on the mass consumer and are intended to provide a wide range of services to subscribers when using communication both inside buildings and on the street, including when moving by car.
The GSM standard uses TDMA, which allows at a single carrier frequency to place 8 speech channels simultaneously. The river codec RPE-LTP with regular pulse excitation and speech transformation rate of 13 kbps is used as a ripe-LTP speech-forming device.
To protect against errors that occur in radio channels, block and convolutional encoding with interleaving are used. Improving the efficiency of encoding and interleaving at a low MS movement rate is achieved by slow switching of operating frequencies during the communication session process at a speed of 217 jumps per second.
To combat interference fading of received signals caused by the multipath propagation of radio waves in the conditions of the city, equalizers are used in communication equipment, providing alignment of pulse signals with a mean-square deviation of the delay time to 16 μs. The system synchronization system is designed to compensate for the absolute signal delay time to 233 μs. This corresponds to the maximum range of 35 km (maximum cell radius).
To modulate a radio signal, a spectral-efficient GUsstian frequency manipulation with a minimum frequency shift (GMSK) is used. Speech processing B. this standard It is carried out within the DTX DTX Intermittent Transmission System (Discontinuous Transmission).
The GSM standard achieves a high degree of messaging security; The message encryption on the open key encryption algorithm (RSA) is being encrypted.
In general, the communication system operating in the GSM standard is designed for its use in various fields. It provides users with a wide range of services and the ability to apply a variety of equipment for transmitting voice messages and data, call and alarms; K. telephone networks General use (PSTN), data transmission networks (PDN) and digital network integration (ISDN).
Below are the main features of the GSM standard:
MS transmission frequency and BTS reception, MHz 890-915;
MS reception frequency and BTS transmission, MHz 935-960;
Duplex separation of frequencies of reception and transmission, MHz 45;
Message transfer rate in the radio channel, KBIT / C 270,833;
Speed \u200b\u200bCodec transformation rate, KBIT / C 13;
Communication channel bandwidth, 2000;
Maximum number of communication channels 124;
GMSK modulation type;
Modulation index BT \u003d 0.3;
Premodulant bandwidth
gausovsky filter, kHz 81.2;
The number of jumps in frequency per second 217;
Maximum cell radius, km to 35;
Channel organization circuit Combined TDMA / FDMA;
Required carrier / interference 9 dB.
Equipment nets GSM. Includes mobile (radiotelephones) and base stations, digital switches, management and maintenance center, various additional systems and devices. The functional interface of the system elements is carried out using a series of interfaces. The structural circuit (Figure 1.1) shows the functional construction and interfaces adopted in the GSM standard.

Figure 1.1 - GSM standard network block diagram
MS consists of equipment that is intended for organizing access to GSM subscribers to existing networks Communication. As part of the GSM standard, five MS classes are received: from a 1-class model with an output power up to 20 W, installed on vehicles, to a 5-class model with a maximum output power up to 0.8 W (Table 1.1). When sending messages, an adaptive transmitter power adjustment is provided that ensures the required communication quality. MS and BTS are independent of each other.
Read also:
Multi-stage AC amplifier with feedback
Electronic devices - devices The principle of action of which is based on the use of phenomena associated with moving flows of charged particles. Depending on how controlled ...
Modeling the operation of the receiver of the cyclic sync signal of the equipment of the CSP
Currently, digital methods of transmitting and processing information are becoming increasingly widespread. Most developed countries are manufactured and constantly being improved ...
Project Intrazonova Volp on the Khabarovsk section - Amursk
Modern optical communication cables (OK) are almost displaced by traditional copper-binding cables in all areas of the interconnected network of Russia. So, the construction of new l ...



































