Instructions
If you are using Internet Explorer 6 or 7, proceed as follows: first, go to the menu on the chain Tools -> Internet Options -> Connection. In case you are using Dial-up, select the required one, then click "Settings". Otherwise, click on the "Network Settings" button, which is located in the "Settings local network».
Now you need to check the box next to the "Use a proxy server" option, in the "Address" field enter the name of the proxy server you have chosen and in the port field, respectively - the proxy port number. If necessary, check the box next to the option "Do not use a proxy server for local addresses", and also click on the "Advanced" button, and then specify the parameters for various protocols. At the end of the settings, click on the "Ok" button two times: the first time to close the Dial-up or local network settings window, and the second time - the Internet settings window. Ready.
If you prefer to work in the Opera 9 browser, go through the menu chain Tools -> Options -> Advanced. Now go to the "Network" tab located in the section on the left. Click on the "Proxy Servers" button, then specify the appropriate proxy servers for the protocols. At the end of the configuration, enable the use of a proxy by checking the appropriate boxes: HTTPS, HTTP, and so on.
Web browser Google chrome appeared on the IT-products market not so long ago, but has already managed to win the trust of a number of users. It works according to the "Install and Use" principle, but before starting work it is better to make a few changes to the program settings.
The main purpose of the browser is to view Web pages. Even a small program that takes only a few tens of kilobytes can cope with this task. The first browsers were like that. However, during the fierce competition that erupted between the leading programs Netscape Navigator and Microsoft Internet Explorer, both programs have acquired a lot of additional customizable features. In particular, Internet Explorer, emerging from the battle as a winner, has turned into a huge software package that allows you to customize the program to the individual requirements of the most biased user. In this article, we will cover most of the settings that are present in the sixth version of Internet Explorer. These settings allow you to change the program interface, add the necessary panels and buttons, change the display parameters of the requested pages. This article discusses how to customize various viewing modes, including disabling graphics, changing the font size, changing the color and encoding of the text of the pages being viewed. From this article, you will also learn how to configure the required privacy and security mode, how to operate with certificates, how to select the size of the folder for storing temporary Internet files, determine the connection to a particular proxy server, and much more.
Toolbar customization
First of all, let's turn to the point View the control menu, which provides access to the most frequently used settings.
On the menu View you can add and remove panels as you wish (fig. 1).
To add or remove buttons on standard toolbars, change their size and order, run the command Toolbars à Setting, as a result, a panel will appear (Fig. 2) where you can change the icons.
On the menu View you can also customize the various browser panes: Search, Favorites, etc. (fig. 3).
Typically, the developers of a Web site determine the size and style of the fonts on the page. However, these parameters may not be optimal for you. You can set your own text display mode in the browser settings. For this in the menu View point the mouse cursor to Font size and select the required size (fig. 4).
You've probably come across a situation when, instead of the text of the page, the browser displays a set of unreadable sequence of characters. In this case, you should check if your browser has selected the correct encoding for this page. Cyrillic (KOI8-R) and Cyrillic (Windows) encodings are often confused.
Most Web pages contain information from which the browser can set the required language encoding.
If there is no such information on the web page, and Internet Explorer is configured with the automatic selection function, then the encoding will be selected automatically.
In order to enable the automatic encoding selection function, you must in the menu View Internet Explorer (Fig. 5), check the box in paragraph Auto select.
If using autoselection it was not possible to determine the correct language encoding, but you know which encoding is needed in a particular case, you can select it manually using the command Additionally.
General Tab
in the tab General(Figure 6) you can define the so-called "Home page", that is, the page from which you will start browsing Web resources.
Temporary Internet Files
As you know, to speed up viewing of pages that you have already visited, they are cached on your computer's hard drive and stored for a certain time in the Temporary Internet Files folder. This storage arrangement speeds up the display of frequently visited Web pages because the browser can open them from your hard drive rather than requesting them again from the Internet.
In order to evaluate what resources are available directly from your computer, open the folder Favorites, run the command File à Work offline and pay attention to your panel Favorites. Site names that are not available in offline, will turn gray, and those whose information is cached on the hard disk will be highlighted in black (Figure 7).
Obviously, the more space you provide on your computer for cached pages, the more likely it is that the newly requested information will be saved on your disk. In order to increase the Internet cache, go to the tab General to section Temporary Internet Files and select the item Options, as a result of which the panel of the same name will appear (Fig. 8), in which you can configure the value of the maximum allowable folder size for storing temporary Internet files.
Increasing the space reserved for the folder storing temporary files may increase the likelihood of previously viewed Web pages being cached on your computer, but it will obviously decrease the amount of free disk space.
In the next screen of the wizard (Fig. 10), you can set the mode in which the subscription will also occur to those pages that will be linked to. base pages... Moreover, you can set the depth of the links.
Next, you will be prompted to select a method for synchronizing the page (Fig. 11). There are two options: by the "synchronize" command or by using a new schedule.
If you choose the "new schedule" mode, the wizard prompts you to define the synchronization frequency and specify the synchronization time (for example, every day at 23:00).
Privacy Tab
Internet Explorer protects the user's privacy and the security of his personal identification information.
Internet Explorer privacy tools include:
- security settings that determine how cookies are handled;
- Privacy Alerts informing you that a Web site you are opening does not match your selected privacy settings.
- the ability to view the privacy policy of the P3P Web site (Platform for Privacy Preferences Project, P3P.
Due to the support of RZR, servers that collect information about visitors (primarily online stores) and ignore this format may be blocked.
The category of confidential information protected by P3P includes the user's personal data: his real name, e-mail address etc. Protected information is also information about the web resources visited, recorded in cookies.
To ensure compatibility with the P3P protocol, a web resource must describe its privacy policy, that is, determine what information about users it records, how it stores it, and what cookies it creates. This description is formalized in accordance with the P3P specification and placed in the root directory of the site. Internet Explorer reads this file and receives the necessary information.
The main channels for leakage of confidential information are third-party sites (they are also called third-party sites), that is, sites to which the user addresses in parallel with the site being viewed. Any Web site that does not appear in a browser window is called a third party. The Web site you are browsing may contain content from third-party Web sites, which in turn may use cookies.
In Internet Explorer 6.0, the default security level is to block cookies from third-party sites that:
- incompatible with P3P, that is, they did not declare their privacy policy;
- request personal information without the explicit consent of the user;
- request personal information without the user's implicit consent.
To change privacy settings, in the tab Confidentiality move the slider up to increase the level of protection and down to set more low level protection (fig. 14). The description of the adjustable modes is given in the table.
It should be noted that changing the privacy mode does not affect the cookies already stored on your computer.
By pressing the button Additionally on the panel (fig. 14), you will go to the panel where you can define Extra options Privacy: disable the automatic handling of cookies and define the mode of acceptance of first-party and third-party cookies (Figure 15).
Security tab
Internet Explorer divides the Internet into zones of different security levels, which allows you to assign the required level of protection to each Web site.
Local intranet (Local Zone)
Typically, this zone contains all addresses that do not require a proxy server to access. The default security level for the local intranet zone is Medium. Therefore, Internet Explorer will allow cookies from Web sites in this zone to be stored on your computer and read by the Web sites on which they were created.
Internet Explorer privacy settings let you control how cookies are handled for all Web sites or for each Web site individually.
Reliable nodes
The Trusted Sites zone is set to low security by default. Internet Explorer will allow cookies from Web sites in this zone to be stored on your computer and read by the Web sites on which they were created.
Limited nodes
For this zone, the default is high level security. Internet Explorer will block all cookies from Web sites in this zone.
Contents Tab
Access limitation
If you use a computer at home and are afraid that your children can view those pages that you want to restrict access to, you can use the settings located on the tab Content on the panel Internet options(fig. 19).
You can restrict access to thematic groups of sites or set a strict ban on access to specific sites.
It is quite difficult to protect a child from visiting all sites of a certain subject, but if you have information about specific sites to which you want to block access, it is naturally much easier to do this. For example, in the tab Allowed nodes you can specify a list of sites that are prohibited from viewing (Fig. 20).
Authentication problem
Authentication is the foundation of communication security. Users must be able to prove that they are who they say they are, and at the same time must be sure that their correspondents, in turn, do not impersonate someone else. It is more difficult to do this online than in real life, primarily because we, as a rule, cannot personally meet with the partner providing this or that online service. However, even in the case when you see your partner, the problem of identification does not disappear - which is why there are passports, driver's licenses, etc. To authenticate partners on the Web, you must have the appropriate certificates. Before talking about the settings, let's recall the purpose of the certificates.
Certificates
A certificate is a document that identifies the owner or security of a Web site. It is a set of data that allows you to identify a correspondent. Certificates are used to protect personal identity on the Internet and to protect your computer from unsafe software.
An organization with a high trust status can issue certificates that allow a public key to be associated with the identity of its owner. Such an organization is called a Certification Authority (CA), or certification authority.
Internet Explorer uses two types of certificates: personal certificates and Web site certificates.
A personal certificate is used to verify the identity of a user who visits a Web site that requires a certificate. A Web site's certificate validates its identity to clients who request a service from it.
A Web site "identity" certificate is required, for example, when sending confidential information over the Internet to a Web site or downloading software from the website.
The basis of authentication is public key encryption. The certificate maps an identifier to a public key. The corresponding private key is known only to the owner of the certificate, who uses it to digitally sign or decrypt the data encrypted with the corresponding public key.
The digital signature on the certificate is the electronic identification of the user, which informs the recipient that this information really came from a specific correspondent and was not changed at the delivery stage. When a user accesses a secure Web site, the latter will automatically send the user its certificate. As a result, the user will receive a notification that the connection is secure and the data transmitted by the user will not be available to third parties (Fig. 21), while when requesting more detailed information from the IE browser, it will explain the mode of visiting the protected site (Fig. 22) ...
To be able to send encrypted or digitally signed messages yourself, the user needs to obtain a personal certificate and configure Internet Explorer to work with it.
Checking Web Site Certificate When Downloading Software
There may be several situations when it is important for you to know that the server with which you are going to exchange data belongs to exactly the company to which it considers itself. Let's take a common example - buying or downloading free software from the Internet.
When you buy boxed software in a regular (non-electronic) store, you receive a sealed box with the product, so you can track if the packaging is not broken, and in most cases you do not doubt who produced the software product. Another thing is when you download a product from the web. In this case, you do not know whether the supplier of this software is exactly who it claims to be, and the downloaded software does not contain viruses, is complete, reliable, etc.
Decide this problem Allows the introduction of an Authenticode into the Distributable Product. This technology empowers software developers through the use of digital signature include information about the developer in the distributed programs. When users download software that is signed with an authentication code and certified by a CA, they can be sure that they are receiving the software from the company that signed it and that the software has not been changed after signing.
Such a system is the basis for protecting consumer rights, for example, in case of viruses in the code. Based on code authentication, users can securely receive signed ActiveX controls, signed Java applets, and other applications.
Software developers are also interested in authenticating a Web-based product, as this makes it difficult to counterfeit their software.
Any company wishing to distribute software or content over the Internet needs such a system.
Client Microsoft programs such as Internet Explorer, Exchange, Outlook, Outlook Express, come with security systems that already include an authentication system for program code downloaded over the Internet. This is necessary primarily because the aforementioned systems are designed for replenishment from the Net. According to the component model, elements such as ActiveX or Java applets can be downloaded to your computer when you browse a Web site. When a user visits a Web page that needs to play an animation or sound, code is often loaded onto the client machine to perform the required function. In this case, the user runs the risk of downloading a virus or other unsafe code. In order to secure the user, a system of signed applications exists.
If a user of the above client applications encounters an unsigned component, the following will happen:
- if the security system of the application is configured for the "High security" mode - the client application will refuse to download the code;
- if the application security system is configured for the "Medium security" mode, the client application will issue a warning (Fig. 23);
- if, on the contrary, the user encounters a signed applet, the client program will display another message (Fig. 24).
Having received confirmation of the authenticity of the downloaded software, the user understands that, firstly, the software that he is going to download really belongs to the publisher, and secondly, he knows that authentication was provided by such and such a center, and represents where to get Additional information in order of authentication. In this session, users can trust the further download procedure. Users can also select the "Always trust download from this publisher" command to speed up the verification process in the future.
Users can always get additional information about the certificate (Fig. 25).
Installing Publisher Certificates
Certificate issuers create for themselves special, so-called root, certificates that confirm the authenticity of their private keys. Each particular type of certificate has its own root certificate: one for e-mail certificates, one for full personal certificates, and one for servers. Usually browsers come with a set of these certificates.
If, while browsing the Internet, you come across a server with a certificate issued by an unknown publisher, you will be prompted to accept this certificate and, if it contains the root certificate of the same issuer, you will be offered the opportunity to install this certificate and assign actions to servers with certificates received from given publisher.
Using digital certificates can ensure the security of your online transactions because it allows you to associate the identity of the certificate holder with a pair of keys (public and private).
Obtaining a personal certificate
So far, we've talked about the need for servers to prove their authenticity. However, in some cases, servers require confirmation of the client's identity. Therefore, now we will talk about personal certificates. There are several categories of trustworthiness for certificates issued by independent certification authorities.
Personal certificates are used to verify the identity of a user at the request of some sites that provide a particular service. Certificates are issued by the same certificate issuers, that is, a third party trusted by both the user and the service operator.
To obtain a certificate, you must register with the certificate issuer of your choice.
Usually, to obtain a certificate, you need to provide the issuer of certificates by mail, and sometimes personally, certain documents, and then pay for the certificate.
The procedure for obtaining a certificate is as follows: you go to the certificate issuer's Web server, fill in the data required to obtain a specific certificate, and select the length of the private key (preferably at least 1024 bits). Before submitting the form, your browser will generate a public (public) and private (private) key pair and enter them into a password-protected database. Private key known only to you - it should not be known to anyone else, including the certification center. On the contrary, the public key is sent along with other entered data to the certification authority for inclusion in the certificate. It is impossible to determine the pair of the public key - the private key.
After issuing a certificate, the certification authority usually sends you a certificate or specifies a URL where you can download it. After downloading the certificate from the certificate issuer, the browser automatically starts the installation procedure.
Installing and Removing Certificates
Internet Explorer has a certificate manager - Internet Explorer Certificate Manager (Figure 26).
It allows you to install and remove client certificates and certificates of certification authorities, or, as they are also called, CA (from the English Center Authority). Many CAs already have root certificates preinstalled in Internet Explorer. You can choose any of these pre-installed certificates to verify the authenticity of the code, the validity of the time stamped in the documents, secure mail, etc. In order to install or remove certificates, go to the tab Content... Select item Certificates and then the corresponding tab. The following tabs are available: Personal, Other Users, Intermediate Certification Authorities, Trusted Root Certification Authorities, etc.
Certificates in category Personal have matching private keys. Information signed by means of personal certificates is identified by the user's private key. By default, Internet Explorer places all certificates that identify a user (using a private key) into a category Personal.
In the tab Trusted Root Certification Authorities usually, root certificates are already preinstalled, which you can view and get all information about them: by whom they were issued, their validity period, etc. (fig. 27).
By clicking on one of the certificates, you can get additional information about it, including the composition and the certification path (Fig. 28).
Setting up a proxy server in Internet Explorer
As you know, modern browsers such as Internet Explorer and Netscape Navigator have internal cache settings that allow you to determine the amount of disk space on your machine that will be used to cache documents you have already viewed. The browser periodically refreshes the documents in the cache to keep them fresh. However, the amount of cache on a PC is usually small, since PC users rarely allocate more than a gigabyte of disk space for caching, so the amount of stored documents is small. It is difficult to allocate a large amount of memory on a local computer, but this can be done on the provider's proxy server - a computer running a special program that caches data requested by all clients of a given provider. Large providers can allocate tens or even hundreds of gigabytes to their customers. Some users fear, however, that using cached documents from a proxy server, they will receive outdated documents, but there is technology to avoid this.
There are a number of criteria by which a decision on caching on a proxy server is made. For example, if an object is marked as confidential, then it will not be cached. Similarly, there are criteria by which a decision is made about the possibility of sending a cached document to a client's request. For example, if a document has passed the expiration date, the server will not send it to the client, but will request a fresh document. Thus, fresh documents (with an expiration date) are provided immediately, and if the proxy server doubts that the document is fresh, it can ask the Web server if the document has changed. It is possible that an expired document is not actually out of date because it has not been updated, in which case the Web server will respond to the proxy server that the document has not yet been "corrupted" and can be submitted to a client request. In other words, there is every reason to use a proxy server.
In order to set up a connection through a proxy server, go to the tab Connections on the panel Internet options(fig. 32) and instead of paragraph Never use(which you probably had configured if you weren't working through a proxy) select Always use the default connection.
Then refer to item Customization, which will lead to the appearance of the panel shown in Fig. 32.
Check the box Use a proxy server for this connection and enter the proxy server address and port - these addresses should be obtained from your ISP. I use the services of Zenon and in my case it is proxy.aha.ru. Then go to the item Additionally(fig. 33) and indicate One proxy for all protocols.
It should be noted that work through a proxy server is not always optimal. The most obvious example is if you have faster access to some Web server than to a proxy server, then there is no point in accessing a proxy server. Or, for example, if you are debugging Java applets on some server and you need to constantly watch how your software is working correctly, then, of course, you will not be satisfied with downloading previous version applet. The panel shown in Fig. 33 Additionally, Play video, as a result, pages will load faster.
After you have removed the display of images and loaded the page, it will be displayed in a "trimmed" form, as shown in fig. 37. There will be icons instead of pictures. By right clicking on such an icon, you can invoke context menu and view the required drawing.
ComputerPress 11 "2002
Internet Explorer browser settings. Today we will talk about a web browser, namely about a veteran of the Internet swimming, the well-known Internet Explorer.
And so Internet Explorer was developed by Microsoft and built into operating system Windows by default. That is, it is installed along with the installation of Windows itself and is updated automatically if you do not change the settings.
Now a little about him. Like any browser, Internet Explorer has an address bar that can be used not only to access pages but also as a field for entering search queries. By the way, the default search engine for the address bar can be customized according to the user's preference.
Supports Internet Explorer to work simultaneously with big amount tabs, has the ability to create bookmarks and has a large number of additional settings and functions that are often not expected from it, as from the default browser (browser included).
Let's take a look at the simple settings further.
Address bar - used directly for entering site addresses, and for entering search queries. If the addresses are clear, then with search queries a little more complicated. There are many search engines (Google, Bink, Yandex, etc.), in order to set the default one for the search that you are using, you need to go to the settings (click on the gear in the mountain on the right), then select "configure add-ons". In the window that opens, select "search services", select the desired one and click on the "Set as default" button,

if your search engine is not in the list, click on the link at the bottom of the "Find other search services" window and find the desired one in the list and add it.

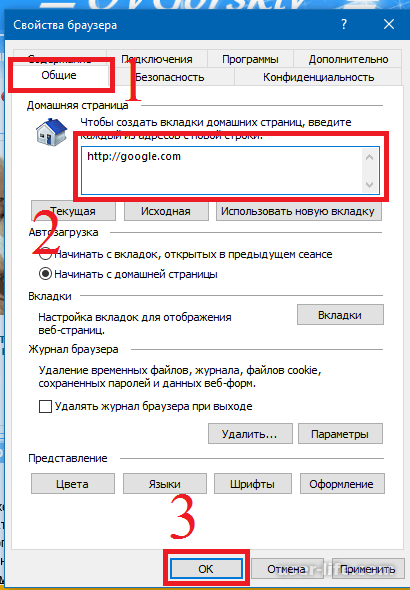
Starting the browser, at startup, each user wants to see his or his pages, which he regularly views, and not offered by default. It is very simple to do this, again go to the settings, select "Internet Options" in the window that opens, the "General" tab, then in the "Home page" field, write your site or sites through Enter, click apply and ok.
An ordinary user, when searching for information, views a lot of sites, so it often becomes necessary to save a link to a site in order to return later. To do this, the site can be added to favorites. It is very simple to do this, when viewing the site, click on the browser settings and select "add site to the list of applications." Now, if you need to quickly go to this site, just click on the star icon next to the settings icon and a list of saved sites will open in front of you.

If we talk about the icons in the mountain on the right (gear-settings, asterisk-selected sites, house-view). Then by clicking on the house we will get to start page or a group of pages that opens in us when the browser starts. This is convenient when you work a lot with one site, in a split second (in one click) you immediately get to it.

In general, we introduced you to the main functions Internet browser Explorer worth setting up for comfortable work in him.
Let's take a look at the IE menu - Tools> Internet Options. The Internet Options window contains seven tabs. The most interesting for us are the General and Connection tabs (Fig. 11.5). The main settings are collected on the Connections tab (Fig. 11.5, on the right). The Install button launches the New Connection Wizard. In the Customization area remote access There are three selectors: Never use, Use when there is no network connection, Always use the default connection. The first selector - Never use - is included when connecting only over a local network.
If you are connecting exclusively via a modem (if you cannot connect to the Internet over a local network), select Use if there is no network connection. Also, this selector is selected for connecting via a modem if it was not possible to connect via the local network. The last selector Always use default connection is selected to connect to the default modem connection.
Internet access can be optimized using a proxy server. Its use is not always required, but desirable. When using a proxy server, the Use proxy server option must be checked. Disabling this option allows you to establish communication "directly", for example, in the event of a proxy server malfunction.
The General tab of the Internet Options window is shown in Fig. 11.5 (left). To shorten the loading time of your browser, we recommend that you click the C blank button in the Home page area. If there is not enough disk space, on the same tab you can use the Delete files button in the Temporary Internet files area or configure their storage settings using the Settings button. The purpose of the standard buttons (Colors, Fonts, Apply or OK) should be clear to you, so we will not dwell on them.
The options on the Programs tab of the Internet Options dialog box should also be straightforward. By default, it has the standard Windows applications used for the HTML editor, Email, newsgroups and Internet calls. If you want IE to be the default browser, check the Check if IE is the default browser option.
IE is fine-tuned on the Advanced tab. Check it out desired parameters in the Customize list. The list is quite extensive - after studying it, you will configure the browser to work with the maximum (just for you) convenience. There is no risk here, since the Restore Defaults button will always allow you to return to the original values.
To switch to Internet Explorer customization mode, in the Control Panel, select the Network and Internet Connections category, and then select the Internet Options icon. As a result, the Internet Properties window will appear on the screen. This window contains the following tabs: General, Security, Privacy, Content, Connections, Programs and Advanced.
Let's consider the procedure for working with each of them.
On the General tab, configure general settings.
In the Address field, indicate the address of the web page, which is selected by the user as a home page. A web home page is a page on the Internet that opens by default every time you start your browser. You can return to this page at any time while browsing the Internet by clicking the Home button on the toolbar or by clicking View Go Home page of the main menu of the Internet Explorer window.
Pressing the C current button allows you to select the home page that is open in this moment... Button C restores the original page as the home page that was set when the browser was installed. If Homepage is not needed, then you should press the empty button. In this case, when you start the Internet browser, it will open empty page, and the Address field will be about: blank To delete temporary Internet files, use the Delete Cookies and Delete Files buttons. Using the Options button, you can switch to the configuration mode and edit the settings for the temporary Internet files folder.
The Options window will appear on the screen. Using the Check for updates of saved pages switch, set the required mode of checking for updates of saved pages. The Temporary Internet Files Folder pane displays the location of the folder that contains the temporary Internet files. In the Use up to disk space field, specify the maximum amount of hard disk space that is intended for this folder.
Using the Move button, you can move the temporary Internet files folder to a specified location; this will open the Browse for folders window, in which, according to the usual Windows rules, specify the required path. To open a folder with temporary Internet files, use the View files button. In the field How many days to keep links on the General tab, indicate the number of days during which the browser should keep links to recently visited pages. Using the Colors button, you can switch to the mode of choosing colors for displaying web pages. Clicking this button will open a window.
Security options
On the Security tab of the Internet Properties window, configure your Internet security settings. At the top of this tab, the Internet zones that are accessible from this local computer... The Security Level area for that zone displays the security level settings for the zone highlighted at the top of the tab. To change these parameters, click the Other button. If necessary, you can restore standard parameters security for each zone. To do this, click the Default button (first, select the icon of the required Internet zone).
Confidentiality
The Privacy tab contains options that you can use to adjust the privacy level of your online experience. The required privacy level is set using the corresponding slider. In this case, to the right of the slider is displayed short description the selected privacy level. By clicking the Advanced button, you can go to the mode for setting additional privacy settings (in particular, in this mode, the processing by the browser is configured Cookies). If necessary, you can configure privacy for individual Web sites.
To do this, use the Change button. When you click it, the Privacy window for individual websites opens, in which the necessary actions are performed. The Contents tab contains options for accessing information obtained from the Internet, options for the auto-fill mode and some personal user data. Using the Settings button, you can switch to the mode of setting the restriction of information received from the Internet. This feature is especially useful for keeping children in check on certain Web sites and their familiarity with certain materials. After clicking this button, the Access Restriction window opens.
When you open this window for the first time, the system will ask you to enter the access password, which should be remembered, since the system will ask for this password on subsequent attempts to enter this mode. Use the Enable (Disable) button to enable / disable established restrictions; you also need to enter the access password. By clicking the Autocomplete button on the Contents tab, you can switch to the autocomplete settings mode. This will open the corresponding window. This window defines the objects for which you want to use auto-fill ( possible options- for web addresses, forms, usernames and passwords in forms), and clears the auto-complete history (using the Clear Forms and Clear Passwords buttons).
If the Request to save password checkbox is selected, the system will ask whether to save the new password after entering it in the field of the web page. If the answer is yes, the password will be saved, and in the future, when you enter the username in the field of the web page, the system will automatically display the password corresponding to this name. To enter some of the personal information about the user provided by certain websites, on the Content tab, click the Profile button.
Connections
The Connections tab contains information about previously configured Internet connections. To create a new computer connection to the Internet, you must click the Install button. As a result, the New Connection Wizard window will appear on the screen (the procedure for creating a new connection is described in the section).
To create a new network connection you should use the Add button, to delete an existing one - the Delete button (first, you need to place the cursor on the object to be deleted). Using the Settings button, you can switch to the mode of viewing and editing the parameters of the network connection selected in the list of connections. To switch to the mode of configuring the parameters of the local network, click the Configure LAN button.
Programs
The Programs tab defines the programs that will be used automatically when working with the Internet. In field HTML editor select the program from the drop-down list that the browser will use to edit HTML files: Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel or Notepad. Depending on the value of this field the corresponding command will be displayed in the File submenu of the Internet Explorer main menu. If Microsoft Word is selected in the HTML Editor field, the Edit In command appears on the File menu. Microsoft Office Word, if Microsoft Excel is selected, the command will be named Edit in Microsoft Office
Excel if Notepad is selected - Edit to Notepad.
- In the Email field, from the drop-down list, select an email program (for example, Outlook Express or The bat!) that Internet Explorer will use.
- In the Newsgroups field, specify the program intended for reading Internet newsgroups that Internet Explorer will use.
The Internet Connection field specifies the dialer to be used by Internet Explorer.
"The Calendar field indicates the Internet calendar program that Internet Explorer will use."
In the Address Book field, select the address book program that Internet Explorer will use. If you check the box
Check if Internet Explorer is the default browser, then every time Internet Explorer is launched, the system will check if this browser is the default. If another Internet browser is used as the default one, the system will offer to restore the use of Internet Explorer in this capacity. Checking this box makes sense if, in addition to Internet Explorer, another browser is installed on the computer.
Additionally
On the Advanced tab, configure additional settings for some browser modes. In particular, using the corresponding checkboxes, you can turn on / off the display of pictures and their frames, playback of animations, sounds and videos on web pages, automatic check Internet Explorer updates, etc. Security settings have been moved to a separate section. If necessary, you can restore the parameters suggested by the system by default: to do this, click the Restore defaults button.
All parameters of this tab, depending on the functional purpose, are divided into groups: Microsoft VM, Security, Multimedia, Configuring HTTP 1.1, Overview, Print, Search from the address bar and Special abilities... Let's dwell on each of them. Microsoft VM In the Microsoft VM group, configure the following settings.
If the Log Java language check box is selected, the browser will keep a log of all active Java programs.
- If the Use Java Jit Compiler check box is selected, then when you visit a web site that uses Java programs, the browser will automatically create such programs and launch them. In other words, this flag enables Internet Explorer to use the built-in Java compiler.
It is recommended to select the Java language scoreboard enabled checkbox if you plan to test Java programs. The settings made with the Use Java Jit Compiler and Java Language Scoreboard enabled checkboxes take effect only after the computer is restarted.
Security
- Additional security settings are configured in this group.
- By checking the boxes SSL 2.0, SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0 enable the mode in which the browser will send and receive confidential information using protocols SSL 2.0, SSL 3.0 and TLS 1.0, respectively. In doing so, the following must be taken into account:
- SSL 2.0 is supported by all secure websites;
SSL 3.0 is more secure than SSL 2.0, but some Web sites do not support it;
- TLS 1.0 protocol has a degree of protection comparable to that of the protocol
- SSL 3.0; this protocol some web sites do not support.
- By selecting the Enable Integrated Windows Authentication check box, enable Integrated Windows Authentication. The setting of this parameter takes effect only after the computer is restarted.
If you select the Enable profile check box, the browser will display requests from websites to provide them with information from the user profile. If you uncheck this box, the browser will not transmit information about the user and, accordingly, display requests from web sites.
- By selecting the Do not save encrypted pages to disk checkbox, they prohibit saving confidential information in the folder with temporary Internet files. It is recommended to set this mode if several users have access to the computer.
- If you select the Warn about switching security mode check box, the browser will notify you when you switch between safe and insecure Internet sites.
By checking the Signature check box for downloaded programs, enable the download programs authentication mode. - If you select the Check server certificate revocation check box, Internet
- Explorer will check the validity of peer certificates on the Internet. - This setting takes effect only after restarting the computer.
- If you select the Delete all files from the temporary Internet files folder when the browser is closed check box, the Temporary Internet Files folder will be automatically cleared when Internet Explorer is closed.
Multimedia
The following parameters are configured in this group.
If you select the Enable automatic image resizing check box, the browser will reduce the size of oversized images on web pages. The checkbox Play animations on web pages enables / disables the mode of playing animations on web pages. Some web pages containing animation load very slowly, and to speed up their loading, it is advisable to select this checkbox.
Using the Play video on web pages and Play sounds on web pages check boxes, enable / disable the playback modes of video and sounds on web pages, respectively. By clearing the Display pictures check box, you can turn off the display of graphic images in order to speed up the loading of web pages. If you select the Show picture frames check box, the picture frames will be displayed when pictures are loaded. This will allow you to get an idea of the location of the elements of the web page before it is fully loaded. Enabling this mode makes sense only when the Show pictures checkbox is selected.
By checking the Improved color rendering checkbox, enable the
smoothing images. HTTP 1.1 Configuration Two parameters are configured in this group. By selecting the Use HTTP 1.1 check box, enable the mode of using the HTTP 1.1 protocol when connecting to web sites.
If you select the Use HTTP 1.1 over proxy connections check box, the browser will use the HTTP 1.1 protocol when connecting to web sites through a proxy server.
Overview
The following parameters are configured in this group. If you select the check box Automatically check for Internet Explorer updates, the browser will periodically check for Internet new version programs. If a new version is found, a corresponding message will appear and the browser will ask you to confirm its download. If you select the Include display styles for buttons and other controls on web pages check box, the browser will apply the settings to render web pages Windows screen(see section 3.1).
If you select the Enable personal favorites menu check box, links that have not been used for a long time will not be displayed in the Favorites submenu of the main menu of the Internet Explorer window. To go to them, you need to click on the arrow located at the bottom of the menu. If you clear the Enable third-party browser extensions check box, the browser will not be able to use tools designed for Internet Explorer but not developed by Microsoft. This setting takes effect only after restarting the computer. If you select the Enable on-demand installation (Internet Explorer) check box, Internet Explorer will automatically download and install the required components to complete a task.
If you select the Show detailed http error messages check box, then if an error occurs when connecting to a server, the browser will display detailed information about the error and advice on how to fix it. If this check box is cleared, the browser will only display the error code and name.
By checking the box
Use built-in auto-complete enables the mode to auto-complete web addresses in the address bar as you type them. In this case, the browser uses previously entered addresses that partially or completely coincide with the desired one. If you clear the Use the same window to load shortcuts check box, web pages opened using links from any document or program other than Internet Explorer will be displayed in a new browser window.
If you select the Use passive FTP protocol check box (for compatibility with firewalls and DSL modems), then the browser will use the passive FTP protocol, which does not require determining the IP address of the computer. This mode is considered safer.
Use the Underline links switch to select the required link underline mode:
Always - links are underlined all the time (this mode is set by default); Never - links are not underlined; On hover - links are underlined only when you move the mouse pointer over them. If you select the Show button "Go to address bar" checkbox, then the Go button will be present on the address bar of the browser window.
By checking the Show short links box, enable the mode of brief display of the object address (link, picture, etc.) in the status bar. If this check box is cleared, the object address is displayed in the status bar in full format. If you select the Allow folder views for FTP sites check box, the FTP sites will be displayed as a folder (just like in Explorer). If this check box is cleared, FTP sites are displayed in HTML format (this is the default setting). If you select the Notify when download is complete checkbox, a corresponding message will appear on the screen after the download is complete.
Only one setting can be configured in the Print area. If you select the Print colors and background images check box, then when you print a web page, this will also print. background image... Note that this may reduce print speed and quality depending on the printer you are using. Search from the address bar. This area contains a radio button When searching, which can have the following values. Do not search from address bar - if this value is selected, searches from the address bar are disabled.
To search, you will need to use the Search button located in the toolbar of the browser window.
Show results and go to the most similar node - in this case the search bar will display links to web pages with addresses similar to the one you want. In this case, the browser will open the closest web page to the desired address. Only go to the most similar site - when you select this value, the search results will open the web page with the address closest to the one you are looking for.
Only show results in the main window - in this case, the results of the search performed using the address bar will be displayed in the main window. The following settings configure accessibility for this group. If you select the Always expand text for images check box, then when the Show pictures check box in the Multimedia group is cleared, the space allocated for the picture will be increased to display all the text associated with it. If you select the Move system caret following focus and selection check box, the system caret will move based on focus or selection changes. This setting is important when working with programs that use the system carriage to determine the desired screen area.
If your browser is slow, it doesn't have to be a bad internet connection. 3rd party toolbars, some add-ons, cookies or not best parameters settings can also hinder high browser performance.
Here are some simple steps you can take to optimize your Internet Explorer browser:
More ideas that might be helpful:
Removing toolbars
Many toolbars downloaded and embedded in the browser affect more than just the browser appearance but also slow down the movement of internet traffic.
The browser toolbar is an add-on (extension) added to its interface. While some browser add-ons can enhance your online experience and can be very useful, others have negative consequences. They can easily set themselves to "default" status by bundling with the widely used free apps and they sometimes interfere with or conflict with other software on the computer.

Each toolbar carries its own specialized functions such as search functions, emoticons, music player etc., thus, they will require additional resources for their work.
In order to remove some of the toolbars, you will need to open the list installed programs(in Windows 7, click Start(Start)> Control Panel(Control Panel) and under Programs(Programs) click Removing a program(“Uninstall a program”) - uninstall programs that you never use).
Right-click each toolbar in the list that you would like to remove and select Delete(Uninstall). After you complete this process, the toolbars will be completely removed.
Disable toolbars and add-ons right in the browser
2. Click the button Service(in the form of a gear) in the upper right part of the window, then select Configure add-ins(Manage add-ons).
3. Under the inscription Display(Show) select All add-ons(“All add-ons”).
4. Select each add-on you want to disable and click Disable(Disable).
5. When you're done, close the window and restart your browser.

Clearing cookies and clearing browser cache
Few people remember to do this, and in the end HDD turns out to be overwhelmed with a large amount of data stored by the browser for years.
To clear your browser cache:
1. Open Internet Explorer.
2. Click the button Service(Tools), hover over the item Security(Safety) and select Delete browser history(Delete browsing history). If you do not want to delete the cookies and files of the websites in the favorites list, select the checkbox Save data of selected websites(Preserve Favorites website data).
3. Check the boxes next to the types of data that you want to delete.
4. Click Delete(Delete).

Reset browser settings
Sometimes, when you install a program, it can change your browser settings without your knowledge. You may notice that your browser is behaving strangely.
If Internet Explorer stops responding to commands or works in general, if you encounter error messages saying that Internet Explorer will close, or if you experience a noticeable slowdown, you might want to reset your Internet Explorer settings. To do this, follow the steps below.
1. Start Internet Explorer.
2. Click the button Service(Tools), then select Browser properties(Internet Options).
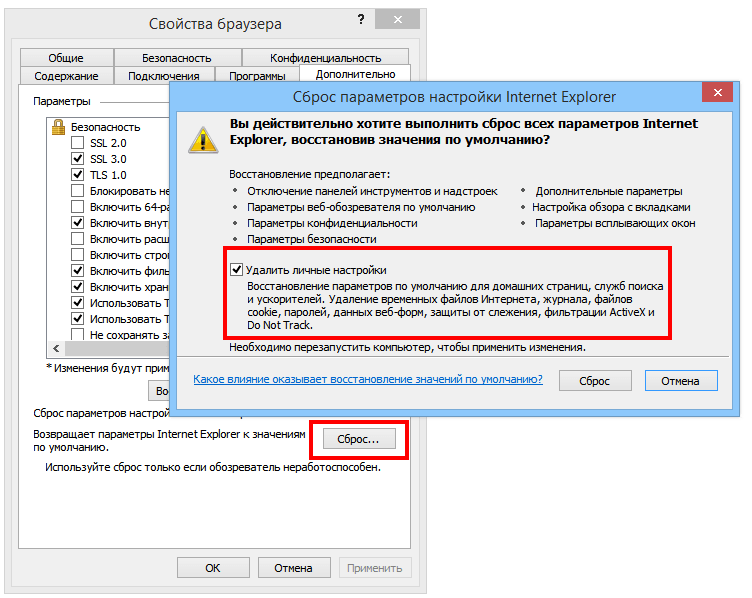
3. In the window Browser properties(Internet Options) click the tab Additionally(Advanced).
4. Click Reset(Reset).
5. In dialogue ResetparameterssettingsInternet Explorer click Reset
Check the box Delete Personal settings
(Delete personal settings) only if you want to delete the browsing history, search service settings, Accelerators, home pages, Tracking protection and ActiveX Filtering data along the way. By checking this box, you are essentially launching a fresh Internet version Explorer.
6. When Internet Explorer finishes switching to default settings, click Close(Close), and then OK.
7. Close Internet Explorer and restart it.
Installing a new version of Internet Explorer
Upgrading to the latest version of Internet Explorer will make Internet access faster. In addition, your computer will be safer and it is very likely that the problems you have with your old browser will go away.
Using the following table, you can find out what the latest version of Internet Explorer you can use in relation to the operating system you are using:
To get the latest version of Internet Explorer, follow this link.
Switching to another browser
There are many internet browsers out there, each slightly different from the others. Some browsers have a lot of features, while others are quite simple in this sense. Some perform slightly better than others. But all internet browsers basically do the same thing: they allow us to browse websites.
The most popular browsers are Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari and Opera. There are also other less popular browsers like RockMelt, Avant Browser, Maxthon, Deepnet Explorer, Flock, SeaMonkey, AOL Explorer, and more.
Switching from one browser to another is in most cases the fastest and easiest way to fix many of the problems we face. If your browser is cluttered with toolbars and plugins, doesn't open some websites, or takes too long to load content, you can try installing a different one and see if it works better.
to install new internet browser, you will need to use the one you already have in order to find and download another. Just use search engine such as Google or Bing to find the browser you want to install and click the download link.
Here are the pages on our site for the most popular browsers that you can use instead of Internet Explorer:
You might also find a guide on how to optimize your Internet speed and performance when using Chrome and Firefox for help.
Based on materials from the Internet portal. Translation into Russian: Alexander Ryabov
And others malware, properly configured browser with the installation of the necessary add-ons and plugins. One of better means protection from all kinds spyware - latest version installed browser such as Internet Explorer 11.
To protect the IE browser, it is advisable to disable unnecessary (or not used) browser settings, possibly vulnerable to external attacks. For advanced security settings, follow these steps:
Turn on pop-up blockers on websites you don't know. This security function allows you to select the desired blocking level. When you visit websites, you will receive pop-up blocking messages. You can also create a list of sites in advance where pop-ups will not be blocked.
The sites on your list will display pop-ups as usual. To enable pop-up blocking, click on the "Tools" button, and select "Browser options". Next, the "Privacy" tab, the "Pop-up blocking" section, where check the "Enable pop-up blocking" box and agree to the changes with the OK button.

Please note that this feature will not block pop-ups from websites within your local intranet or your trusted sites.
To block absolutely all pop-up windows, move the security level slider up. In addition to the default "Medium" mode, there are three more higher degrees of protection.
Protected mode.
Another browser protection setting is Protected Mode. This feature will help prevent malware from running in your browser. To enable Protected Mode, again click the "Tools" icon, "Internet Options". On the Security tab, select the Enable Protected Mode check box and click OK.

Protected Mode is configured separately for all zones: Internet, Local Intranet, Trusted Sites, and Dangerous Sites.
Disable ActiveX.
Internet Explorer's security has been dramatically improved by disabling ActiveX, Active Scripting, and Java. But, in this case, verified sites that also use these functions will not be able to load properly. Add them to your trusted list. To set Internet Explorer to the highest security level, move the slider all the way up and accept the changes with the OK button.
How to enable ActiveX for verified sites.
Click the "Tools" button, go to the "Security" option and check the box "ActiveX Filtering". Now, when you visit a web page with ActiveX controls, Internet Explorer will block them. The ActiveX filtering icon is displayed in the browser address bar. Clicking on the icon will enable the ActiveX for that particular web page.
Disable Java scripting.
Java scripts create interactive web pages, but are also an open gateway for malware. Only include Java scripts for trusted websites. To disable them - the "Security" tab. Click the Custom button and scroll down to the Run Scripts ... Java heading.


































